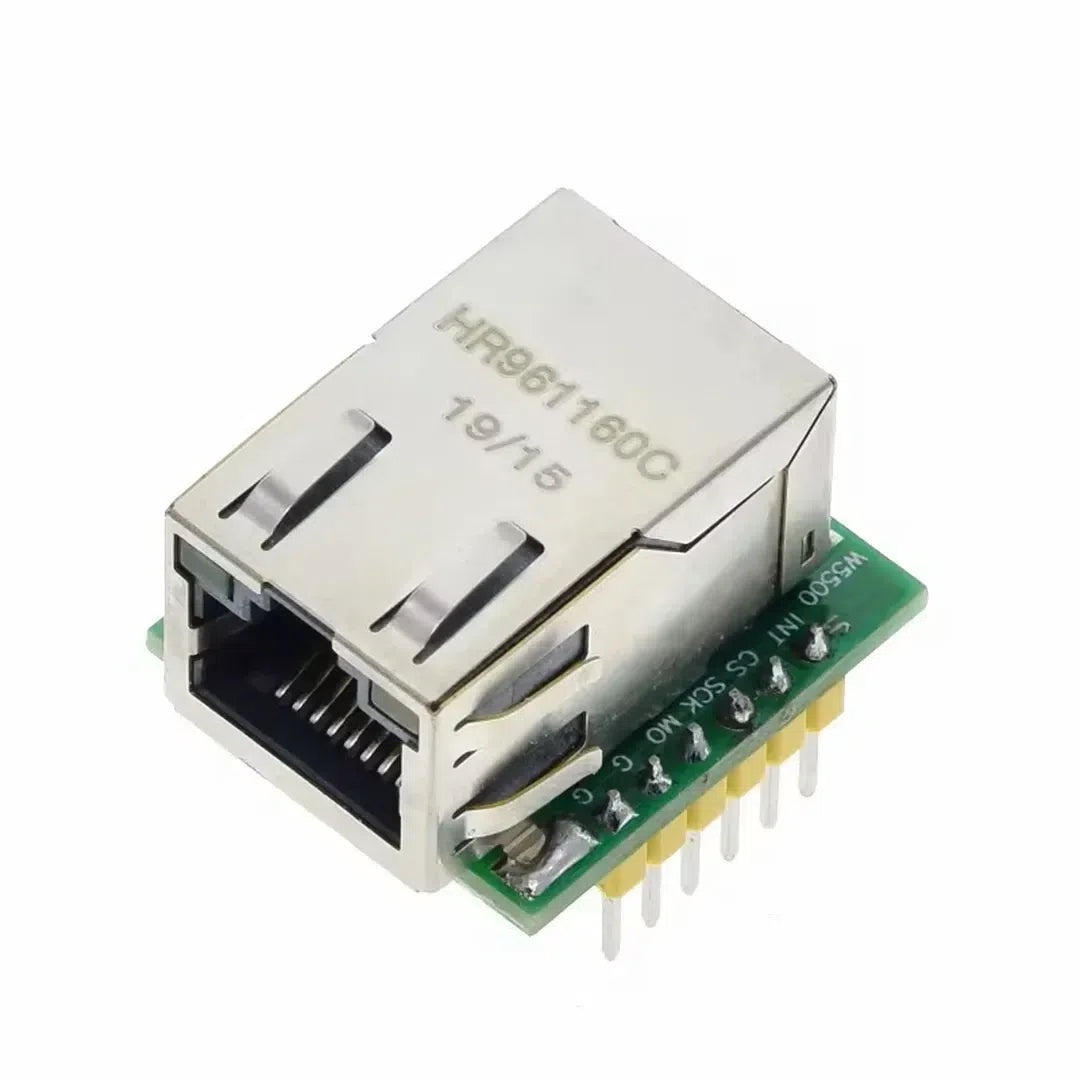
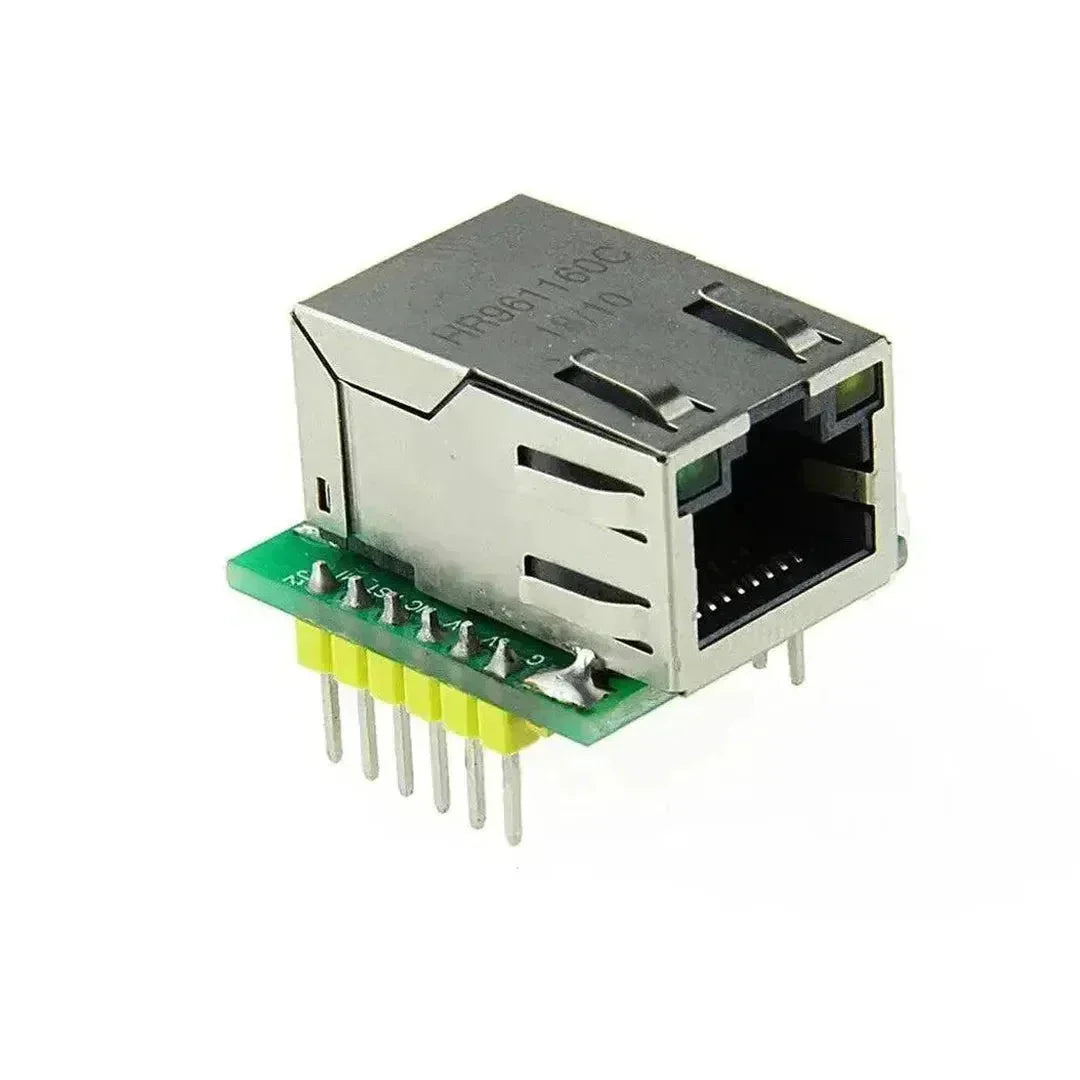
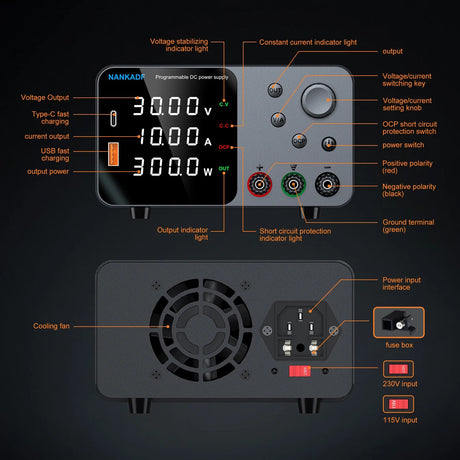
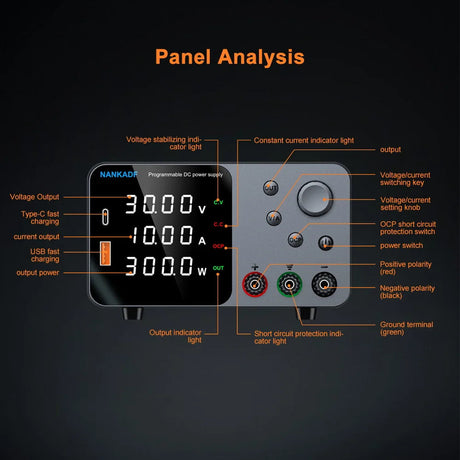
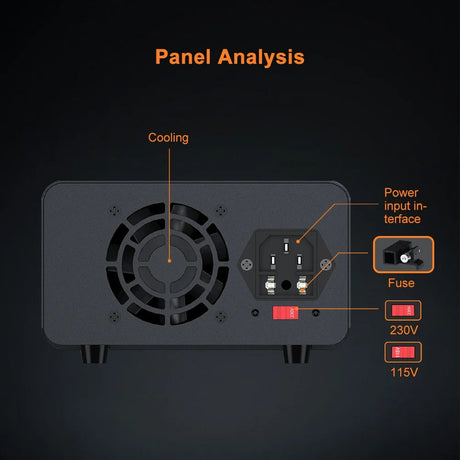
The USR-ES1 is a W5500-based Ethernet module that allows Arduino projects to connect to the internet via a wired connection. It’s compact, reliable, and supports TCP/IP protocols, making it perfect for IoT applications, web servers, and data logging. This tutorial will guide you through using the USR-ES1 W5500 Ethernet module with Arduino.
What You Will Need
- USR-ES1 W5500 Ethernet Module
- Arduino Board (e.g., Uno, Mega, Nano)
- Ethernet Cable
- Breadboard and Jumper Wires
- A computer with the Arduino IDE installed
Step 1: Understanding the USR-ES1 W5500 Ethernet Module
The W5500 Ethernet module is based on the W5500 chip, which supports:
- TCP, UDP, ICMP, IPv4, ARP, IGMP, PPPoE protocols
- SPI interface for communication with microcontrollers
- Up to 8 simultaneous socket connections
W5500 Pinout
| Pin | Function |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power (3.3V) |
| GND | Ground |
| MISO | SPI Data Output |
| MOSI | SPI Data Input |
| SCK | SPI Clock |
| CS (SS) | Chip Select |
| RST | Reset (optional) |
Step 2: Wiring the USR-ES1 W5500 to Arduino
Here’s how to connect the module to an Arduino Uno:
| USR-ES1 Pin | Arduino Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| MISO | Pin 12 |
| MOSI | Pin 11 |
| SCK | Pin 13 |
| CS (SS) | Pin 10 |
| RST | Not connected (optional) |
Note: The W5500 operates at 3.3V. Ensure you don’t connect it directly to a 5V supply.
Step 3: Install the Ethernet Library
To communicate with the W5500 module, you’ll need the Ethernet2 library.
Steps to Install the Ethernet2 Library:
- Open the Arduino IDE.
- Go to Sketch > Include Library > Manage Libraries.
- Search for "Ethernet2" in the Library Manager.
- Click Install.
Step 4: Upload the Code
Here’s an example sketch to set up the W5500 module as a simple web server:
#include <Ethernet2.h>
// Network configuration
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED }; // MAC address
IPAddress ip(192, 168, 1, 177); // Static IP address
EthernetServer server(80); // Port 80 for HTTP
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // Wait for Serial Monitor to open
}
Serial.println("Initializing Ethernet...");
if (Ethernet.begin(mac) == 0) {
Serial.println("Failed to configure Ethernet using DHCP");
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip); // Use static IP if DHCP fails
}
Serial.print("Ethernet IP Address: ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.localIP());
server.begin();
}
void loop() {
EthernetClient client = server.available(); // Check for incoming clients
if (client) {
Serial.println("New client connected");
while (client.connected()) {
if (client.available()) {
char c = client.read();
Serial.write(c); // Print incoming data to Serial Monitor
// Respond to HTTP GET requests
if (c == '\n') {
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println("Connection: close");
client.println();
client.println("<html><body><h1>Hello from Arduino!</h1></body></html>");
break;
}
}
}
client.stop(); // Disconnect the client
Serial.println("Client disconnected");
}
}
Step 5: Test the Setup
- Connect the Arduino to your computer via USB and the W5500 module to your router with an Ethernet cable.
- Open the Arduino IDE and select the correct Board and Port under the Tools menu.
- Upload the code to the Arduino by clicking Upload.
- Open the Serial Monitor (Tools > Serial Monitor) and set the baud rate to
9600. Note the IP address displayed. - Open a web browser and enter the Arduino’s IP address (e.g.,
http://192.168.1.177). - You should see a webpage displaying "Hello from Arduino!"
Troubleshooting
- Ethernet not initializing: Ensure proper wiring and check if the Ethernet cable is securely connected.
- IP conflict: Verify that the static IP address does not clash with other devices on the network.
- No response in the browser: Ensure the IP address in the code matches your network’s subnet.
Applications of the W5500 Ethernet Module
- IoT data logging
- Remote control systems
- Home automation servers
- Sensor networks with web interfaces
Conclusion
You’ve successfully set up the USR-ES1 W5500 Ethernet module with Arduino to create a simple web server. This versatile module enables you to build reliable, wired network-connected projects. Expand this example by integrating sensors, actuators, or databases for more advanced applications!