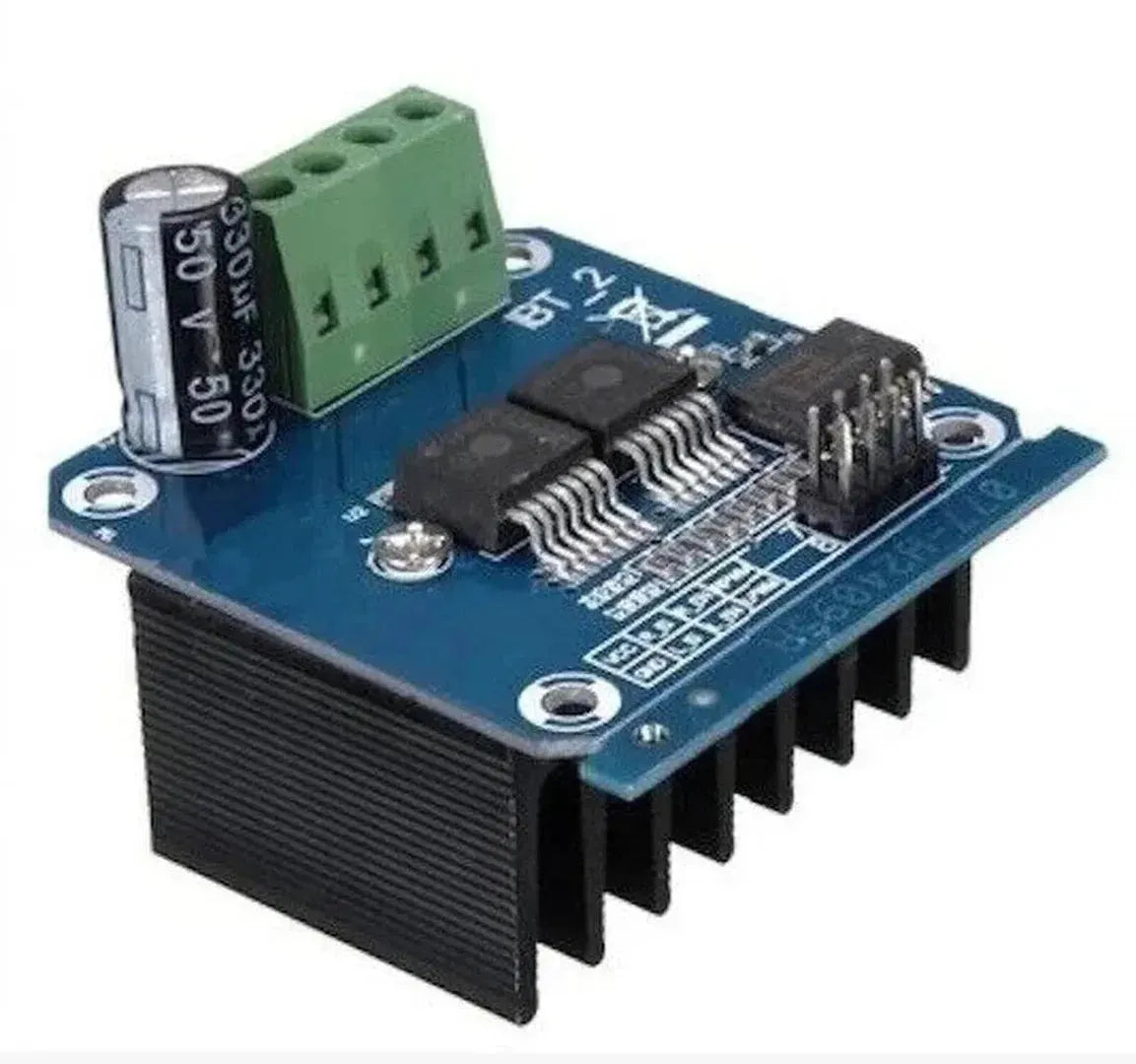
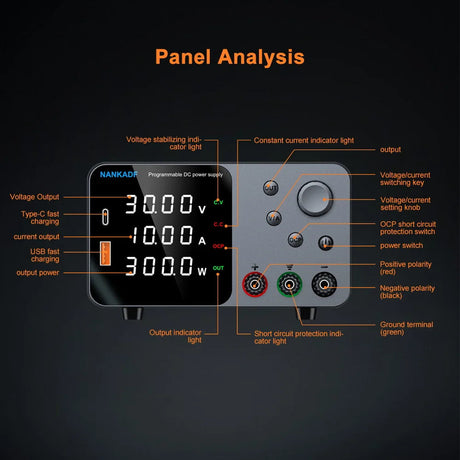
The BTS7960 is a powerful H-Bridge motor driver module that can handle high current and voltage, making it ideal for driving large DC motors. It provides PWM control, overcurrent protection, and efficient heat dissipation, making it perfect for robotics, RC cars, and other high-power motor applications. This tutorial will guide you through interfacing the BTS7960 with an Arduino.
What You Will Need
- BTS7960 Motor Driver Module
- Arduino Board (e.g., Uno, Mega, Nano)
- DC Motor
- External Power Supply for the motor (matching the motor’s voltage)
- Jumper Wires
- A computer with the Arduino IDE installed
Step 1: Understanding the BTS7960 Pins
The BTS7960 module has the following key pins:
| Pin | Function |
|---|---|
| VCC | Logic power supply (5V) |
| GND | Ground |
| R_EN | Right motor enable (active HIGH) |
| L_EN | Left motor enable (active HIGH) |
| R_PWM | Right motor PWM input |
| L_PWM | Left motor PWM input |
| MOTOR_A | Motor terminal A |
| MOTOR_B | Motor terminal B |
| VMS | Motor power supply (voltage input) |
| GND | Ground |
Step 2: Wiring the BTS7960 to Arduino
Below is the wiring guide for connecting the BTS7960 to an Arduino Uno:
| BTS7960 Pin | Arduino Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| R_EN | Pin 4 |
| L_EN | Pin 5 |
| R_PWM | Pin 6 |
| L_PWM | Pin 7 |
| MOTOR_A | Motor Terminal A |
| MOTOR_B | Motor Terminal B |
| VMS | Motor Power (+) |
| GND | Motor Power (-) |
Note: Ensure your external power supply matches the voltage and current requirements of your motor.
Step 3: Upload the Code
Here is an example code to control the motor direction and speed:
#define R_EN 4
#define L_EN 5
#define R_PWM 6
#define L_PWM 7
void setup() {
pinMode(R_EN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(L_EN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_PWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(L_PWM, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("BTS7960 Motor Driver Test");
}
void loop() {
// Forward motion
digitalWrite(R_EN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(L_EN, LOW);
analogWrite(R_PWM, 150); // Set speed (0-255)
analogWrite(L_PWM, 0);
delay(2000);
// Stop
digitalWrite(R_EN, LOW);
digitalWrite(L_EN, LOW);
analogWrite(R_PWM, 0);
analogWrite(L_PWM, 0);
delay(1000);
// Reverse motion
digitalWrite(R_EN, LOW);
digitalWrite(L_EN, HIGH);
analogWrite(R_PWM, 0);
analogWrite(L_PWM, 150); // Set speed (0-255)
delay(2000);
// Stop
digitalWrite(R_EN, LOW);
digitalWrite(L_EN, LOW);
analogWrite(R_PWM, 0);
analogWrite(L_PWM, 0);
delay(1000);
}
Step 4: Test the Setup
- Connect your Arduino to your computer via USB.
- Open the Arduino IDE and select the correct Board and Port from the Tools menu.
- Upload the code by clicking the Upload button.
- Once the code is uploaded, the motor will alternate between forward and reverse motion, with pauses in between.
Troubleshooting
- Motor not spinning: Ensure your motor power supply is connected and matches the motor’s voltage requirements.
- Erratic motion: Check all connections, especially the motor terminals and PWM pins.
- Overheating: If the motor driver overheats, ensure proper heat dissipation and verify that the motor’s current does not exceed the module’s rating.
Applications of BTS7960
- Robotic vehicles
- Conveyor belt systems
- Motorized gates
- High-power motor control in industrial setups
Conclusion
You’ve successfully interfaced the BTS7960 motor driver with an Arduino and controlled a DC motor. This versatile driver is perfect for high-power applications requiring precise control. Experiment with different PWM values to control the motor’s speed and build your own motorized projects!