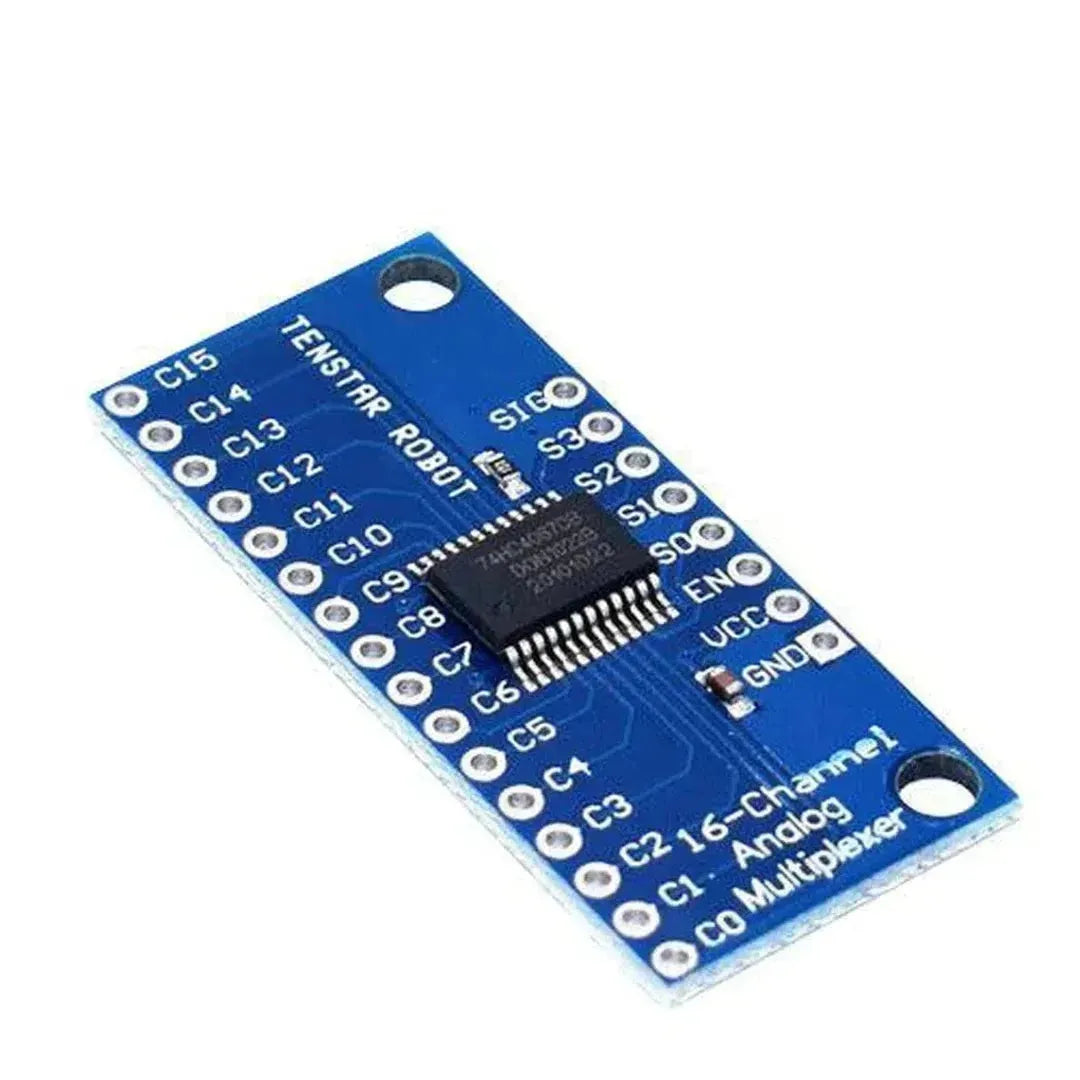
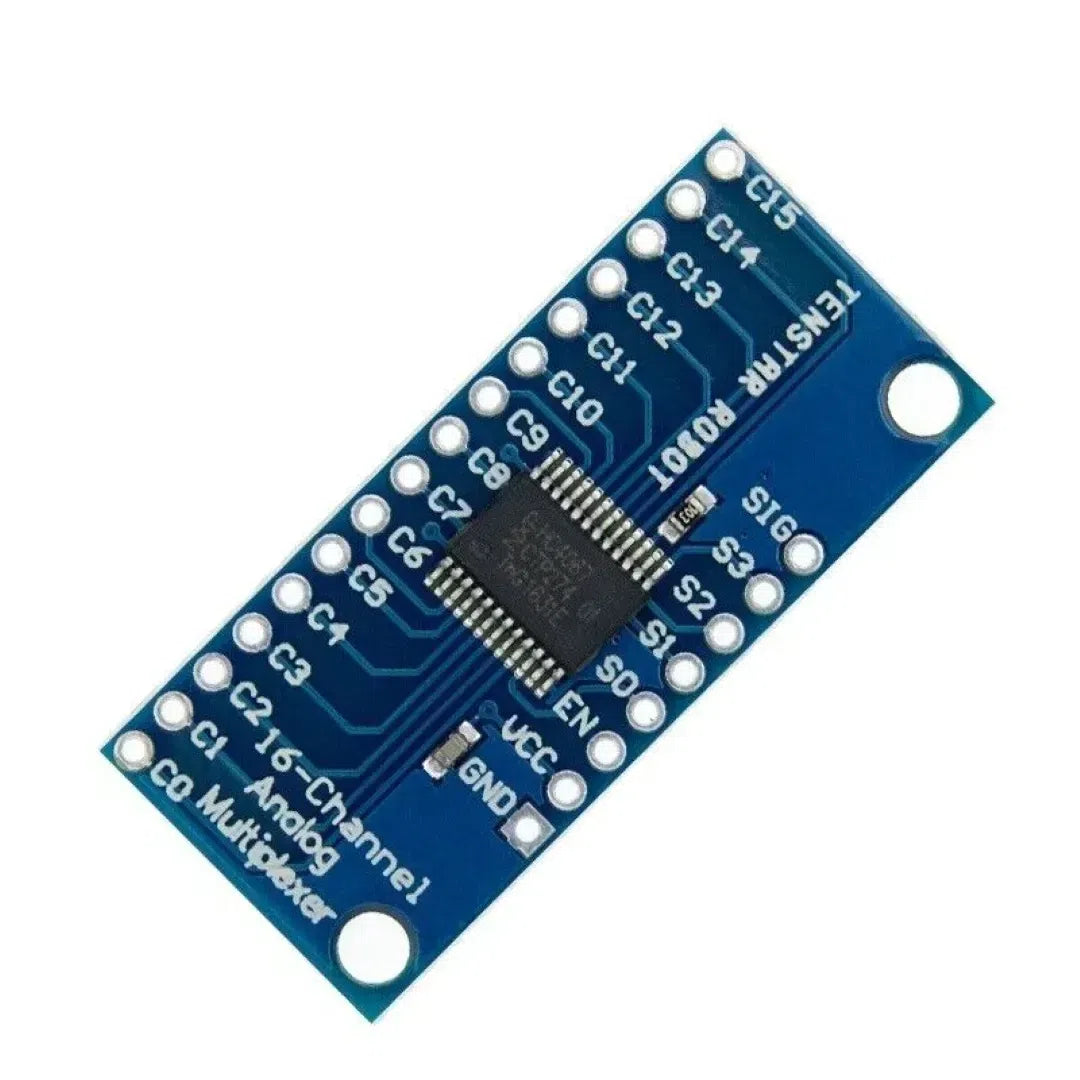
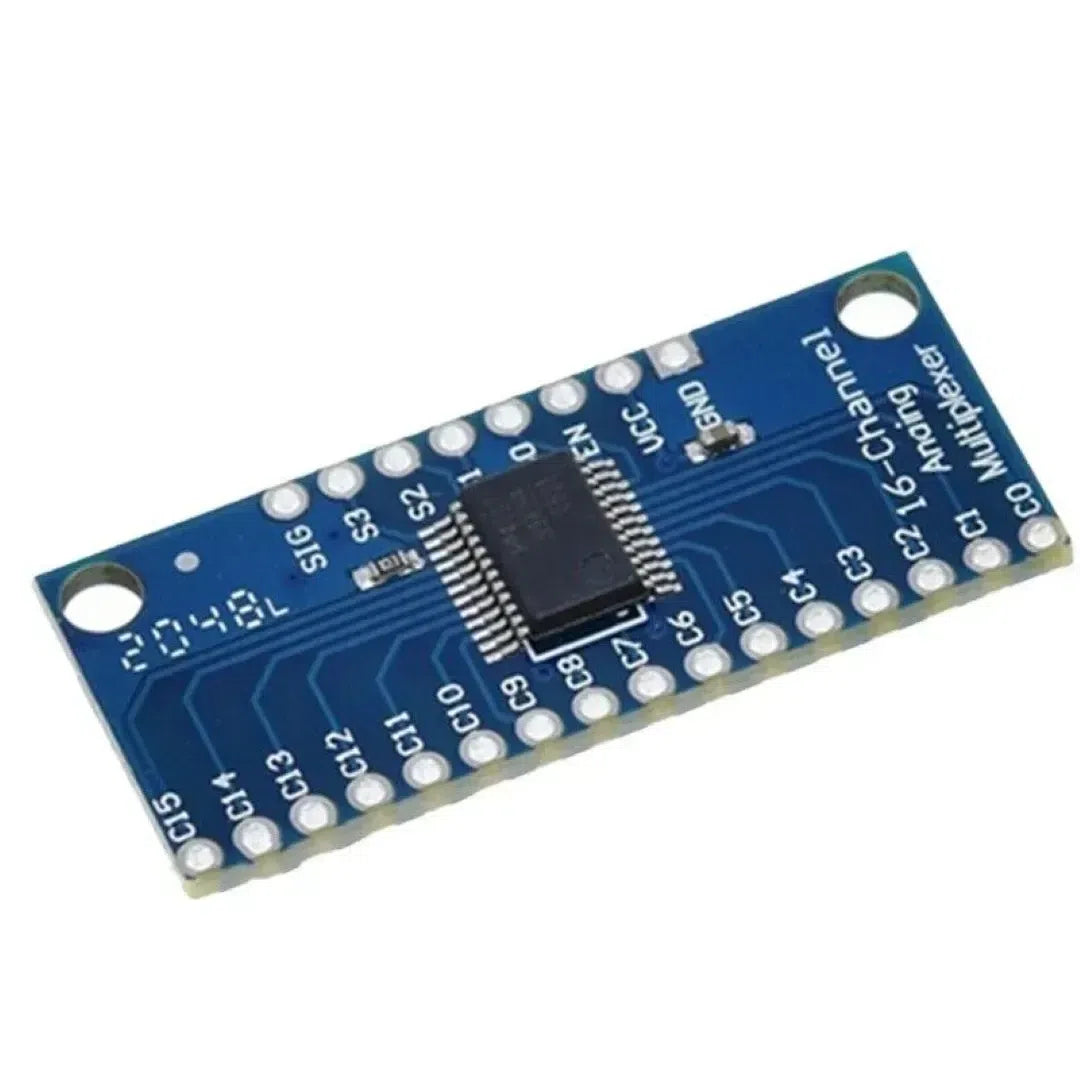
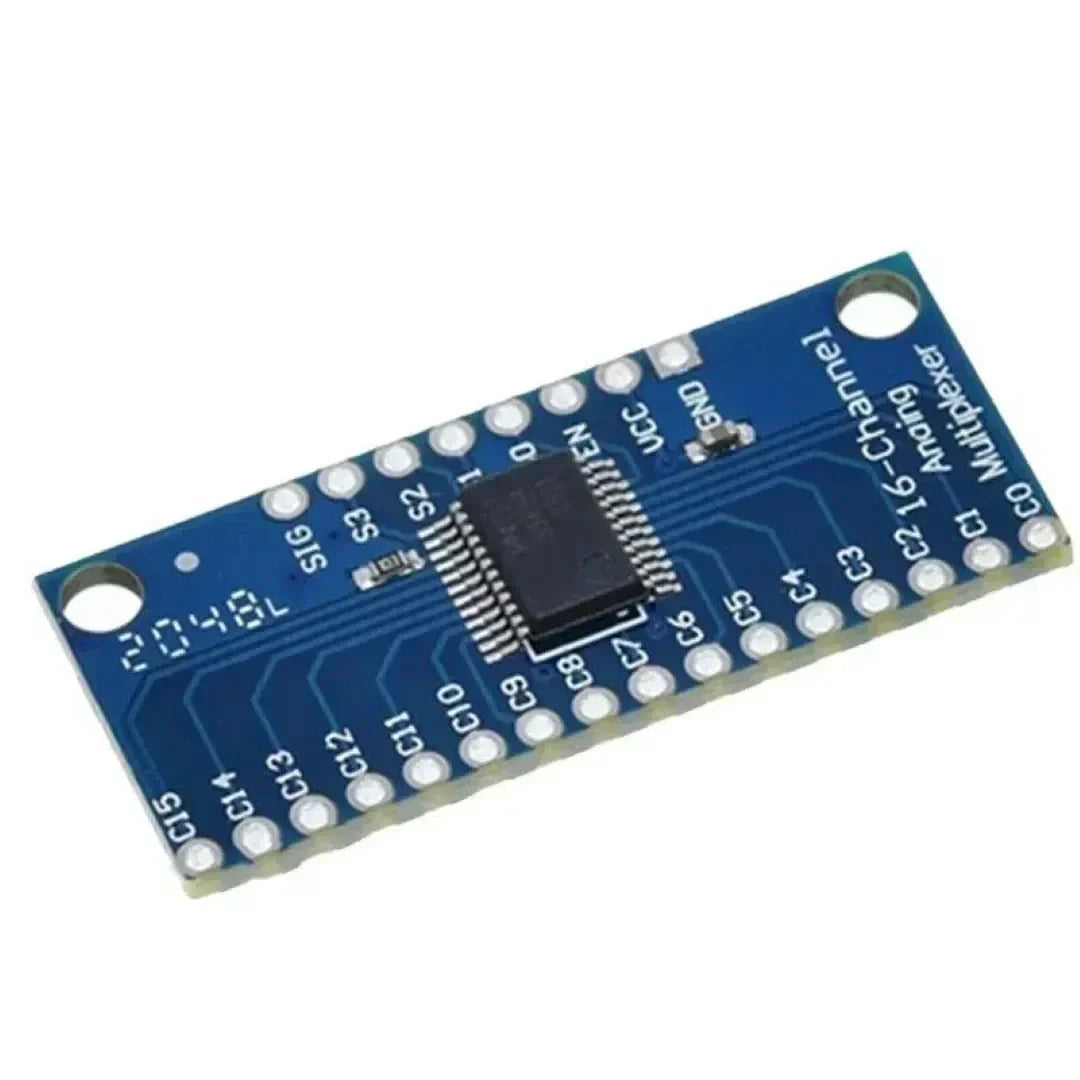
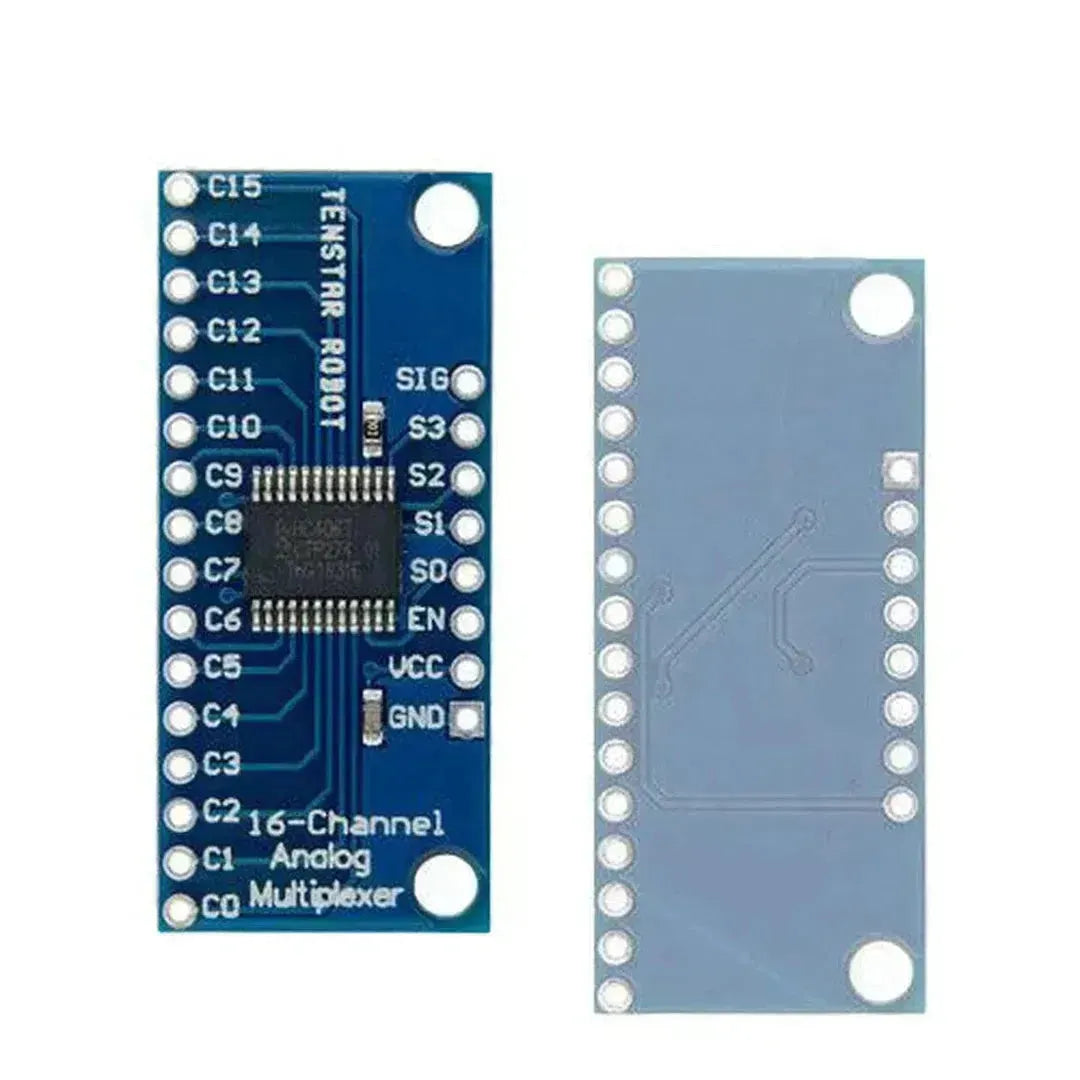
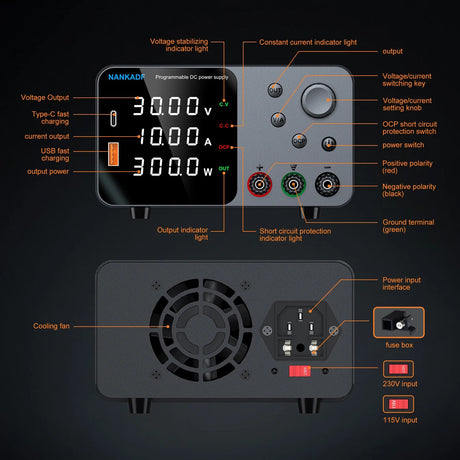
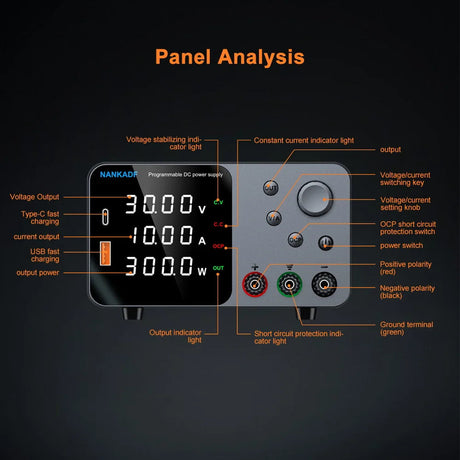
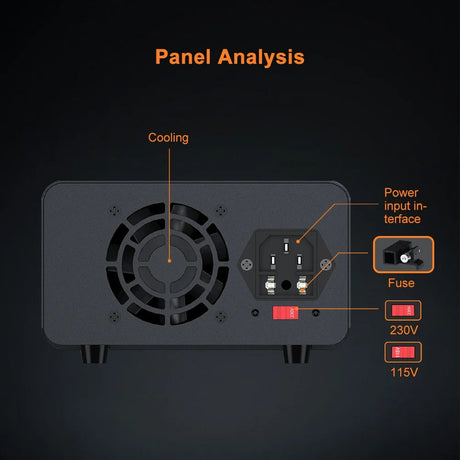
The CD74HC4067 is a 16-channel analog/digital multiplexer that enables a Raspberry Pi to interface with up to 16 inputs or outputs using only a few GPIO pins. It’s perfect for expanding the I/O capabilities of your Raspberry Pi when working with multiple sensors or devices.
What You Will Need
- Raspberry Pi (any model with GPIO support, e.g., Pi 3, Pi 4)
- CD74HC4067 Multiplexer
- Analog or Digital Input Devices (e.g., sensors, switches)
- Breadboard and Jumper Wires
- Python installed on the Raspberry Pi
Step 1: Understanding the CD74HC4067
The CD74HC4067 has:
- 16 Input/Output Channels (S0-S15)
- 4 Control Pins (S0, S1, S2, S3) to select the active channel.
- 1 Enable Pin (EN) to activate the multiplexer (active LOW).
- A single COM (common) pin for shared communication.
Truth Table for Channel Selection
| S3 | S2 | S1 | S0 | Active Channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | S0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | S1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | S2 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | S15 |
Step 2: Wiring the CD74HC4067 to the Raspberry Pi
Connect the multiplexer to the Raspberry Pi as follows:
| CD74HC4067 Pin | Raspberry Pi Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V (Pin 1) |
| GND | GND (Pin 6) |
| S0 | GPIO17 (Pin 11) |
| S1 | GPIO27 (Pin 13) |
| S2 | GPIO22 (Pin 15) |
| S3 | GPIO23 (Pin 16) |
| EN | GND (Active LOW) |
| COM | GPIO18 (Pin 12, Analog Input/Output) |
| S0-S15 | Connect sensors/devices |
Step 3: Install Required Libraries
Update your Raspberry Pi and install Python libraries for GPIO control.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt install python3-rpi.gpio
Step 4: Python Code to Read Data from the Multiplexer
Here’s a Python script to control the CD74HC4067 and read data from the connected channels.
Python Code Example
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
# Define GPIO pins
S0 = 17
S1 = 27
S2 = 22
S3 = 23
COM = 18 # Common pin for input/output
# Initialize GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup([S0, S1, S2, S3], GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(COM, GPIO.IN) # Set COM pin as input for reading data
# Function to select a channel
def select_channel(channel):
GPIO.output(S0, channel & 0x01)
GPIO.output(S1, (channel >> 1) & 0x01)
GPIO.output(S2, (channel >> 2) & 0x01)
GPIO.output(S3, (channel >> 3) & 0x01)
try:
while True:
for channel in range(16):
select_channel(channel)
time.sleep(0.1) # Small delay for channel stabilization
value = GPIO.input(COM) # Read data from the active channel
print(f"Channel {channel}: {value}")
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Exiting...")
finally:
GPIO.cleanup()
Step 5: Applications of the CD74HC4067 with Raspberry Pi
- Reading Multiple Sensors: Interface with up to 16 sensors (e.g., temperature, humidity, or light).
- Expanding Digital I/O: Manage multiple switches, LEDs, or relays.
- Analog Sensor Integration: Read signals from potentiometers, joysticks, or soil moisture sensors.
- Home Automation: Control multiple devices like lights, fans, or appliances.
Troubleshooting
-
No Data from Channels:
- Verify the wiring of S0-S3 control pins and the COM pin.
- Ensure sensors/devices are properly connected to the S0-S15 pins.
-
Incorrect Channel Selection:
- Check the truth table for S0-S3 configurations.
- Ensure the EN pin is connected to GND for activation.
-
Intermittent Readings:
- Add a small delay (
time.sleep(0.1)) between switching channels to allow signal stabilization.
- Add a small delay (
Conclusion
The CD74HC4067 multiplexer is a powerful and cost-effective way to expand the Raspberry Pi’s input/output capabilities. By following this guide, you can easily interface with up to 16 analog or digital devices using just 4 GPIO pins. Experiment with various sensors and applications to make the most of this versatile module! 🚀