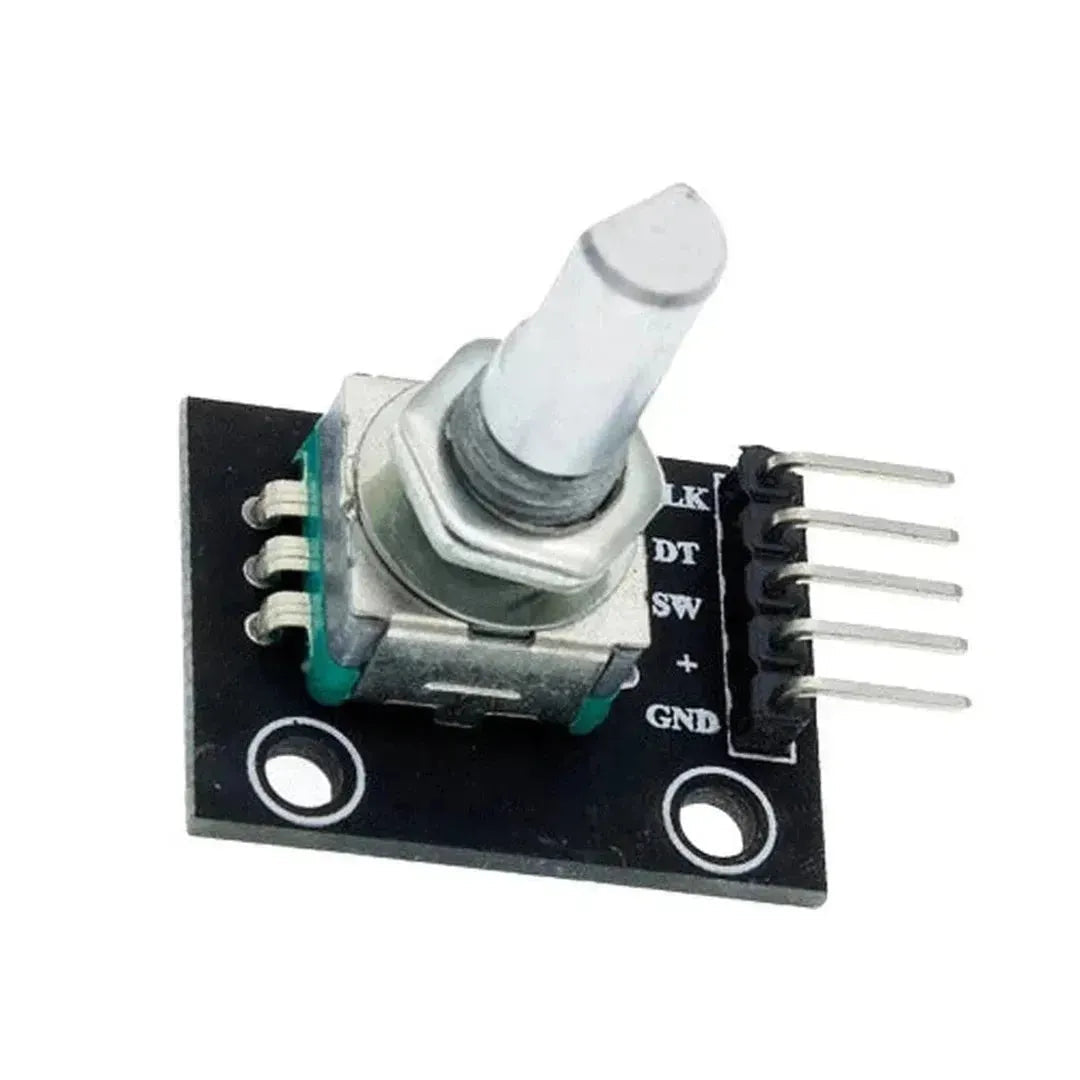
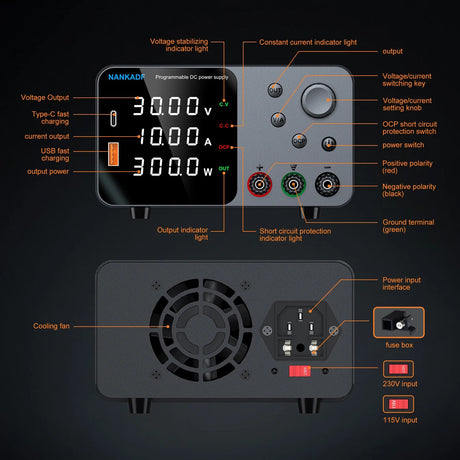
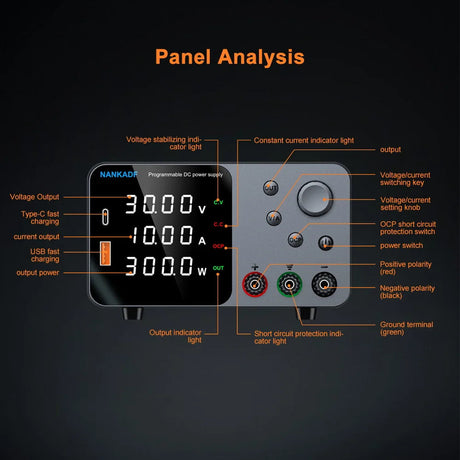
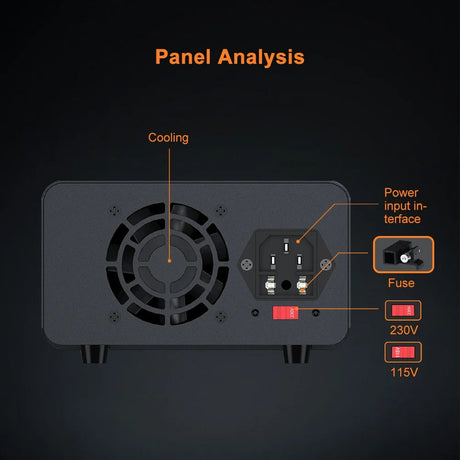
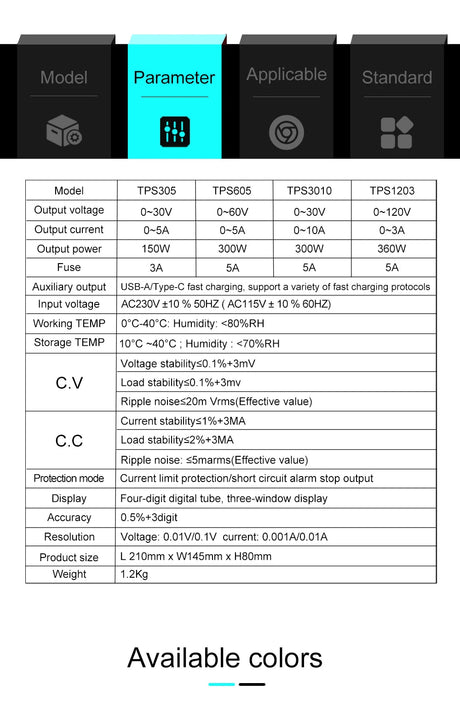
A rotary encoder is a sensor that converts rotational motion into digital signals, allowing precise control over position, speed, and direction. It is commonly used in volume controls, robotics, CNC machines, and menu navigation. This guide will show you how to set up and use a rotary encoder with a Raspberry Pi using Python.
What You Will Need
- Raspberry Pi (any model with GPIO support, e.g., Pi 3, Pi 4)
- Rotary Encoder (e.g., KY-040)
- Breadboard and Jumper Wires
- Python installed on the Raspberry Pi
Step 1: Understanding How a Rotary Encoder Works
A rotary encoder has two main outputs:
- CLK (A) – Clock pulse signal
- DT (B) – Direction signal
- SW (optional) – Push button (used for selecting options)
When rotated, the CLK and DT pins generate pulses. The order of these pulses determines the direction of rotation.
Step 2: Wiring the Rotary Encoder to the Raspberry Pi
| Rotary Encoder Pin | Raspberry Pi Pin | Function |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V (Pin 1) | Power Supply |
| GND | Ground (Pin 6) | Ground |
| CLK (A) | GPIO17 (Pin 11) | Clock Pulse |
| DT (B) | GPIO27 (Pin 13) | Direction Signal |
| SW (Button) | GPIO22 (Pin 15) | Button Press |
Step 3: Install Required Libraries
Update your Raspberry Pi and install the RPi.GPIO library for handling GPIO interrupts.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt install python3-rpi.gpio
Step 4: Python Code to Read Rotary Encoder Input
Basic Python Code to Read Rotation
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
# Define GPIO pins
CLK = 17
DT = 27
counter = 0
last_state = None
# Setup GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(CLK, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(DT, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
# Read initial state
last_state = GPIO.input(CLK)
try:
while True:
current_state = GPIO.input(CLK)
if current_state != last_state:
if GPIO.input(DT) != current_state:
counter += 1
direction = "Clockwise"
else:
counter -= 1
direction = "Counterclockwise"
print(f"Position: {counter}, Direction: {direction}")
last_state = current_state
time.sleep(0.01) # Debounce delay
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Exiting...")
finally:
GPIO.cleanup()
Adding Button Press Detection
# Define button pin
SW = 22
GPIO.setup(SW, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
def button_pressed(channel):
print("Button Pressed!")
# Add event detection for button press
GPIO.add_event_detect(SW, GPIO.FALLING, callback=button_pressed, bouncetime=300)
Step 5: Applications of a Rotary Encoder with Raspberry Pi
- Menu Navigation – Scroll through LCD or OLED menus.
- Volume Control – Adjust volume in media applications.
- CNC Machines – Precise movement control in stepper motor applications.
- Robotics – Detect wheel rotation for speed and position tracking.
- Smart Home Automation – Use as a selector for different home functions.
Troubleshooting
-
Rotary Encoder Not Responding
- Check the wiring and GPIO pin assignments.
- Ensure pull-up resistors are enabled (
PUD_UP).
-
Skipping Steps or Erratic Movement
- Add debounce delay (
time.sleep(0.01)). - Use GPIO interrupts instead of polling (
GPIO.add_event_detect).
- Add debounce delay (
-
Button Press Not Detected
- Ensure button pin is properly connected to GND.
- Add a debounce time of 300ms in
GPIO.add_event_detect.
Conclusion
A rotary encoder is a versatile input device for menu navigation, motor control, and position tracking. By following this guide, you can easily integrate a rotary encoder with your Raspberry Pi for interactive projects. 🚀