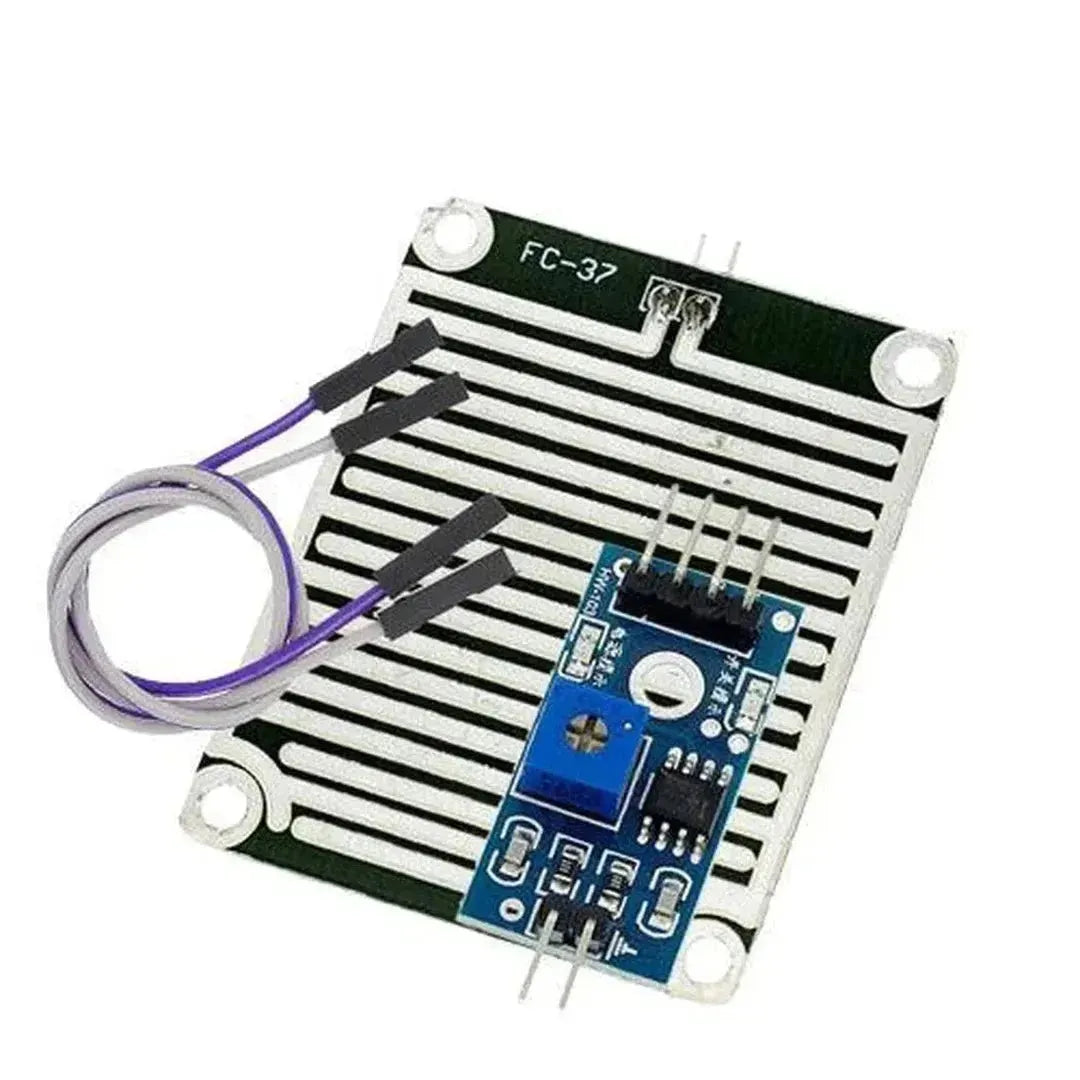
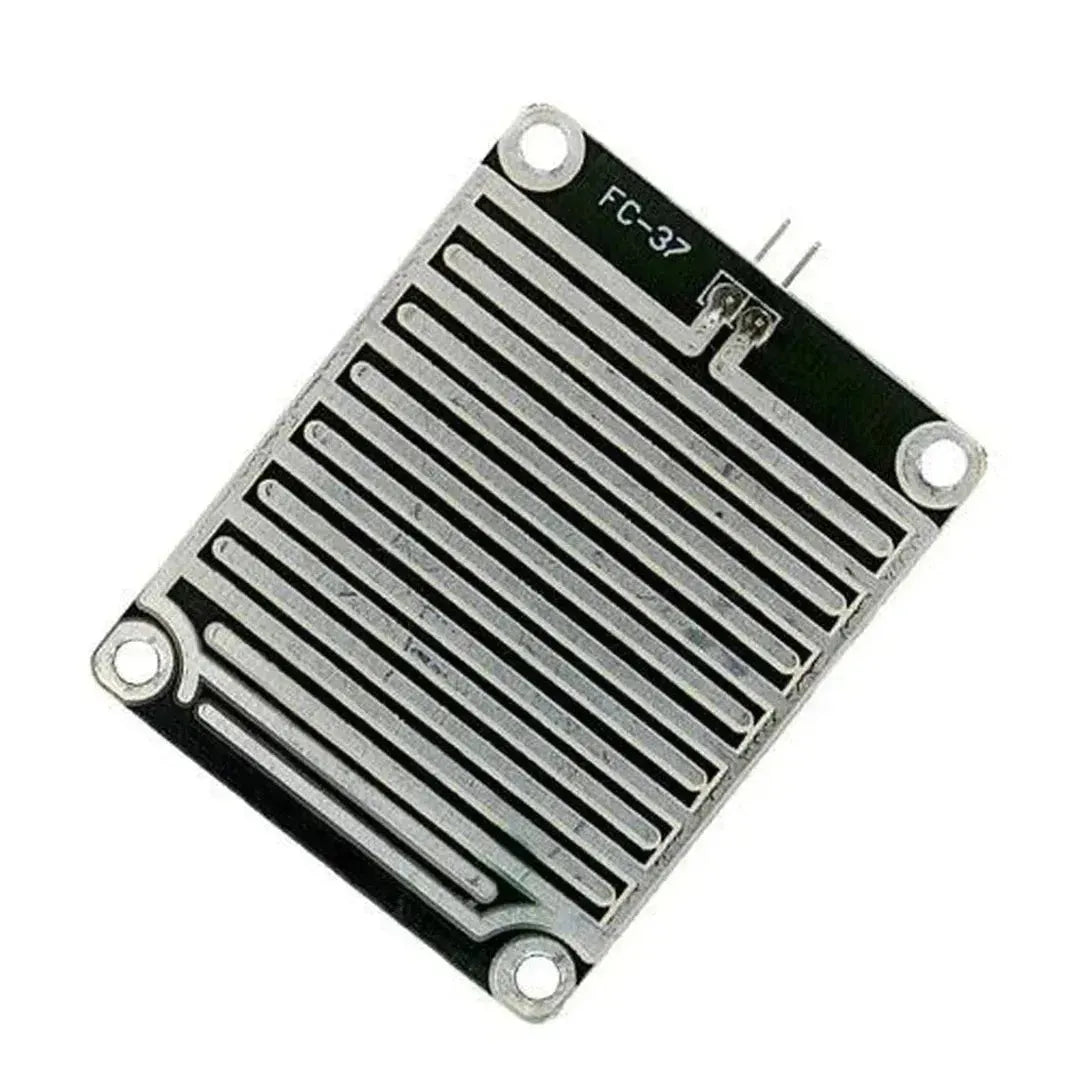
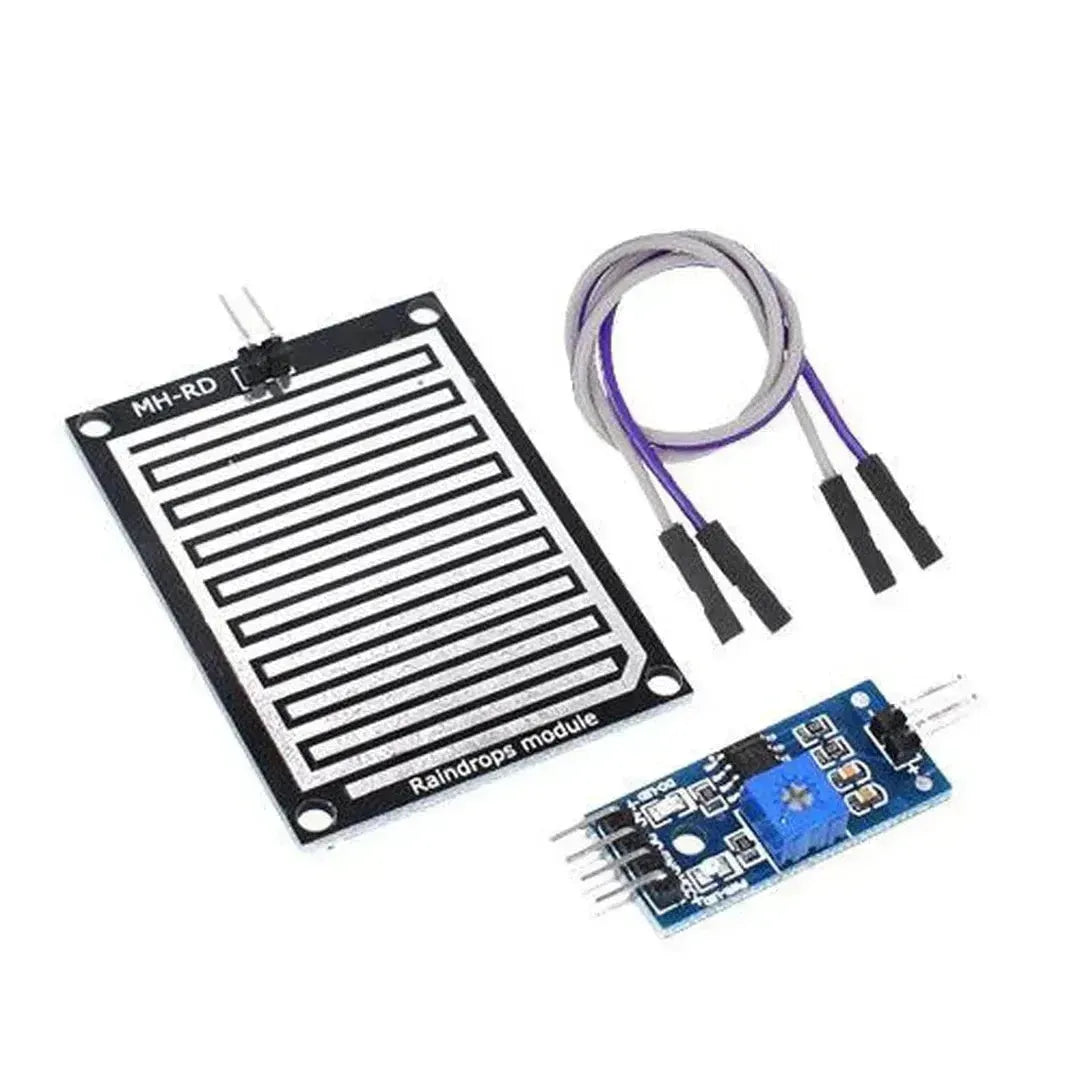
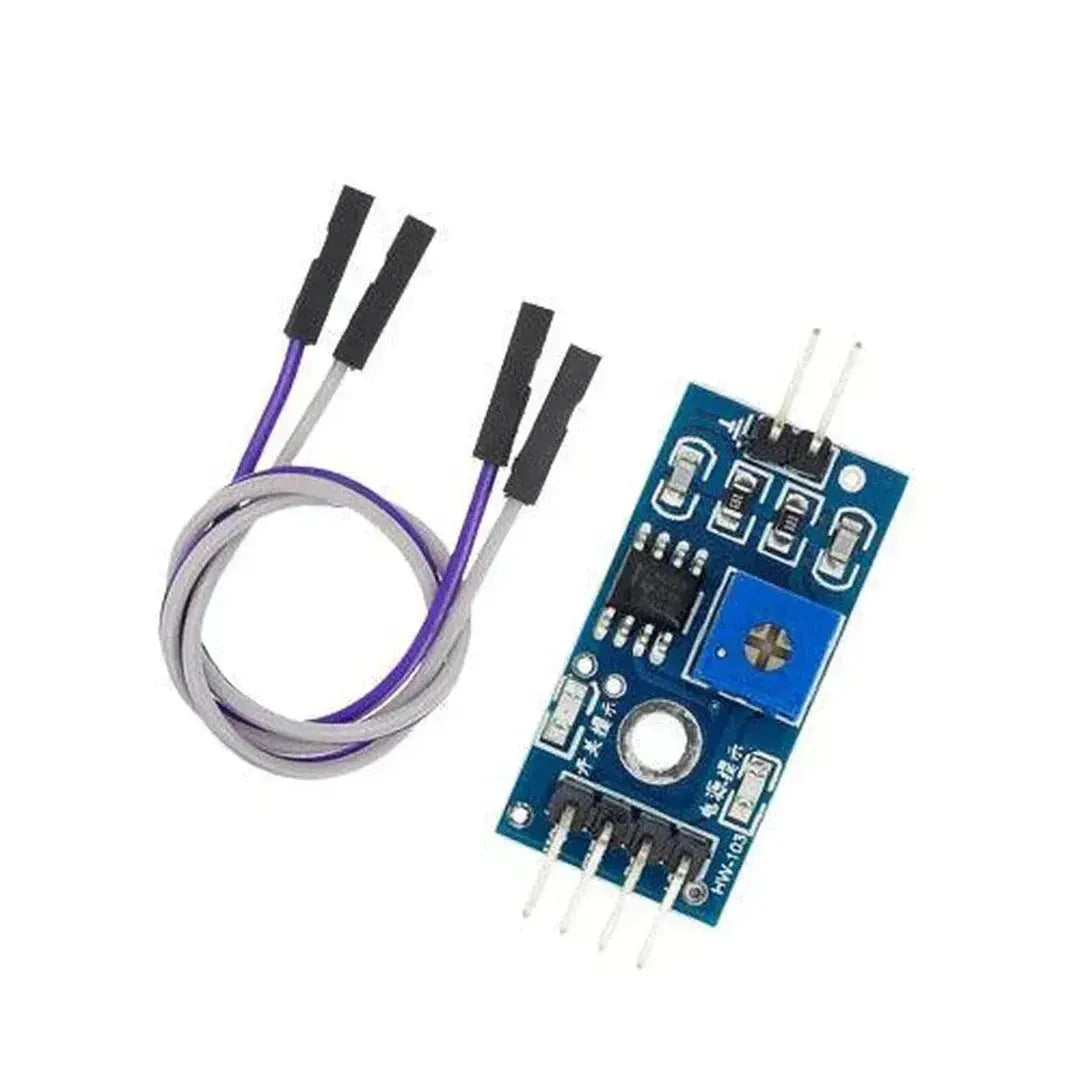
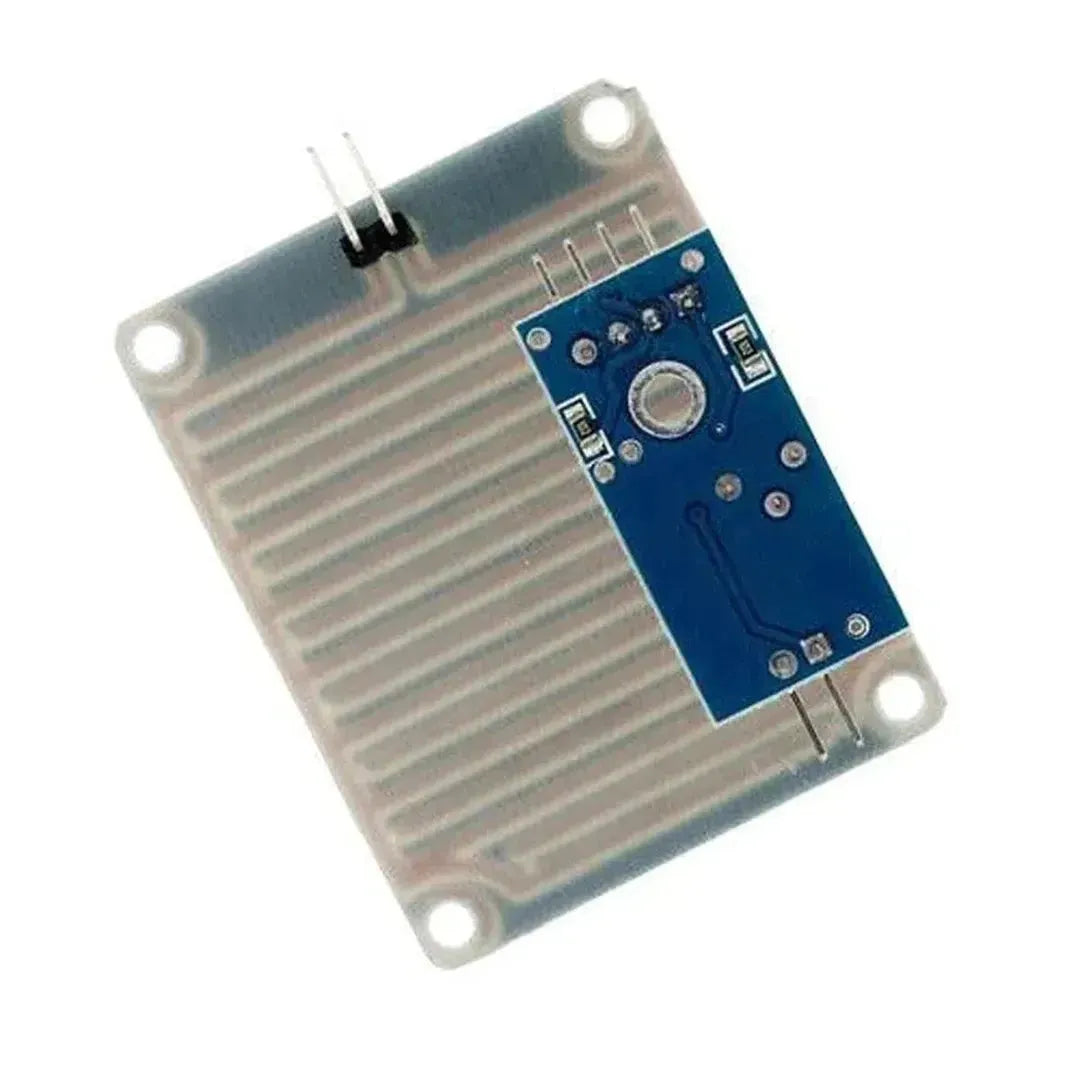
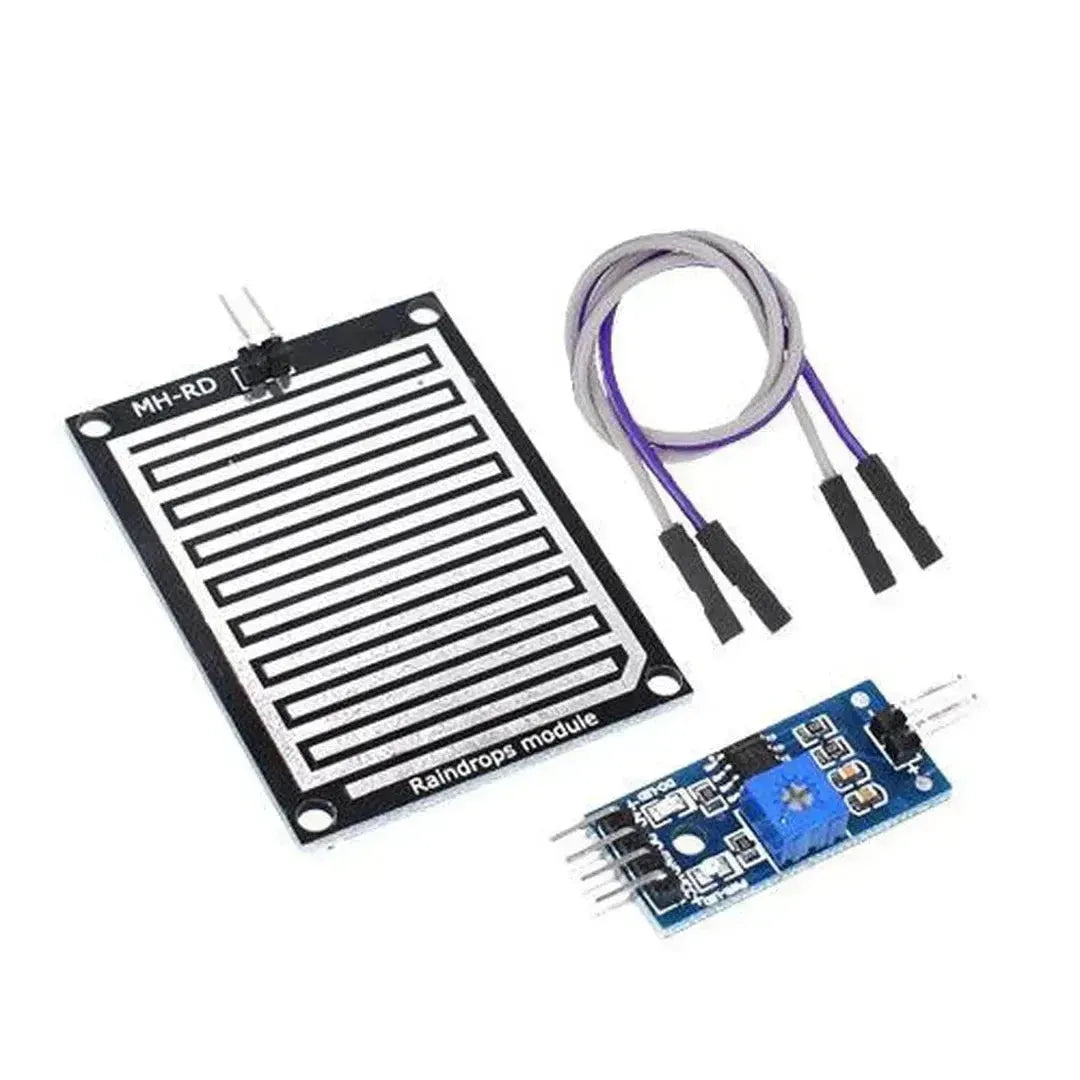
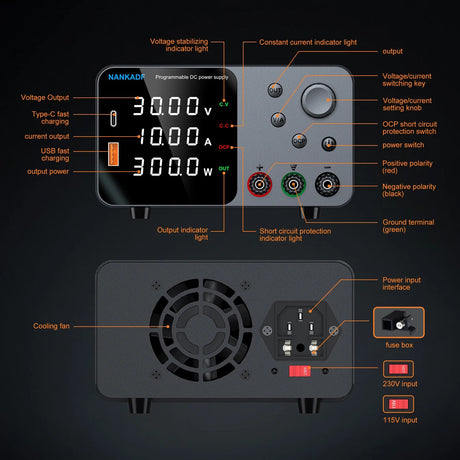
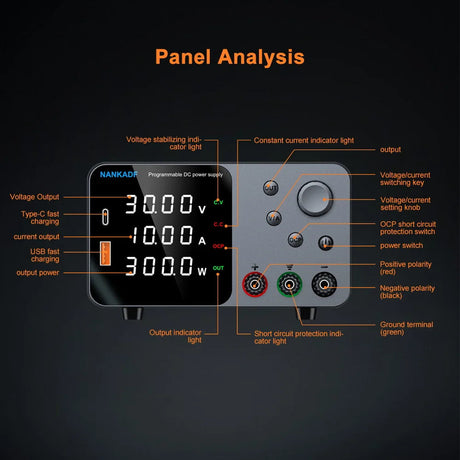
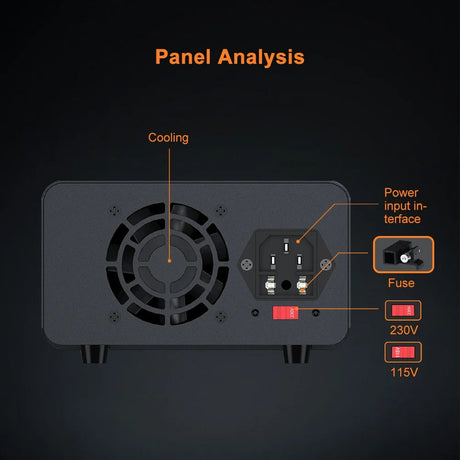
A snow/rain sensor is a device used to detect the presence of snow, rain, or water. It’s often utilized in weather monitoring, smart irrigation systems, and IoT projects. This tutorial will guide you through connecting and using a snow/rain sensor with Arduino.
What You Will Need
- Snow/Rain Sensor Module
- Arduino Board (e.g., Uno, Mega, Nano)
- Breadboard and Jumper Wires
- A computer with the Arduino IDE installed
Step 1: Understanding the Snow/Rain Sensor
A typical snow/rain sensor consists of a detection board and a control module. The detection board has conductive traces that detect the presence of water by measuring resistance changes.
Snow/Rain Sensor Pinout
| Pin | Function |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power Supply (3.3V or 5V) |
| GND | Ground |
| A0 | Analog Output |
| D0 | Digital Output (adjustable sensitivity) |
- Analog Output (A0): Provides a continuous reading of moisture levels.
- Digital Output (D0): Outputs HIGH or LOW based on the set threshold.
Step 2: Wiring the Snow/Rain Sensor to Arduino
Here’s how to connect the snow/rain sensor to an Arduino Uno:
| Sensor Pin | Arduino Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| A0 | A0 |
| D0 | Pin 2 |
Step 3: Upload the Code
Here’s an example sketch to read data from the sensor and display it on the Serial Monitor:
Example Code
#define digitalPin 2 // Connect sensor D0 to Arduino Pin 2
#define analogPin A0 // Connect sensor A0 to Arduino A0
void setup() {
pinMode(digitalPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Snow/Rain Sensor Test");
}
void loop() {
// Read digital output
int digitalState = digitalRead(digitalPin);
if (digitalState == LOW) {
Serial.println("Rain or snow detected!");
} else {
Serial.println("No rain or snow detected.");
}
// Read analog output
int analogValue = analogRead(analogPin);
Serial.print("Analog Value: ");
Serial.println(analogValue);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Step 4: Test the Setup
- Connect the Arduino to your computer via USB.
- Open the Arduino IDE and select the correct Board and Port under the Tools menu.
- Upload the code to the Arduino by clicking Upload.
- Open the Serial Monitor (Tools > Serial Monitor) and set the baud rate to
9600. - Observe the readings from the sensor. When water is present, the digital output will change, and the analog value will increase.
Applications of the Snow/Rain Sensor
- Weather monitoring systems
- Smart irrigation systems
- Water leakage detection
- Automated windshield wipers
Troubleshooting
- No response from the sensor: Ensure proper wiring and verify that the sensor is powered correctly.
- Unstable readings: Avoid excessive vibrations and ensure the sensor is clean.
- Digital output not working: Adjust the sensitivity using the onboard potentiometer.
Conclusion
You’ve successfully interfaced a snow/rain sensor with Arduino, enabling you to detect water presence for various applications. Experiment further by integrating this sensor into automated systems like irrigation controllers or weather stations!