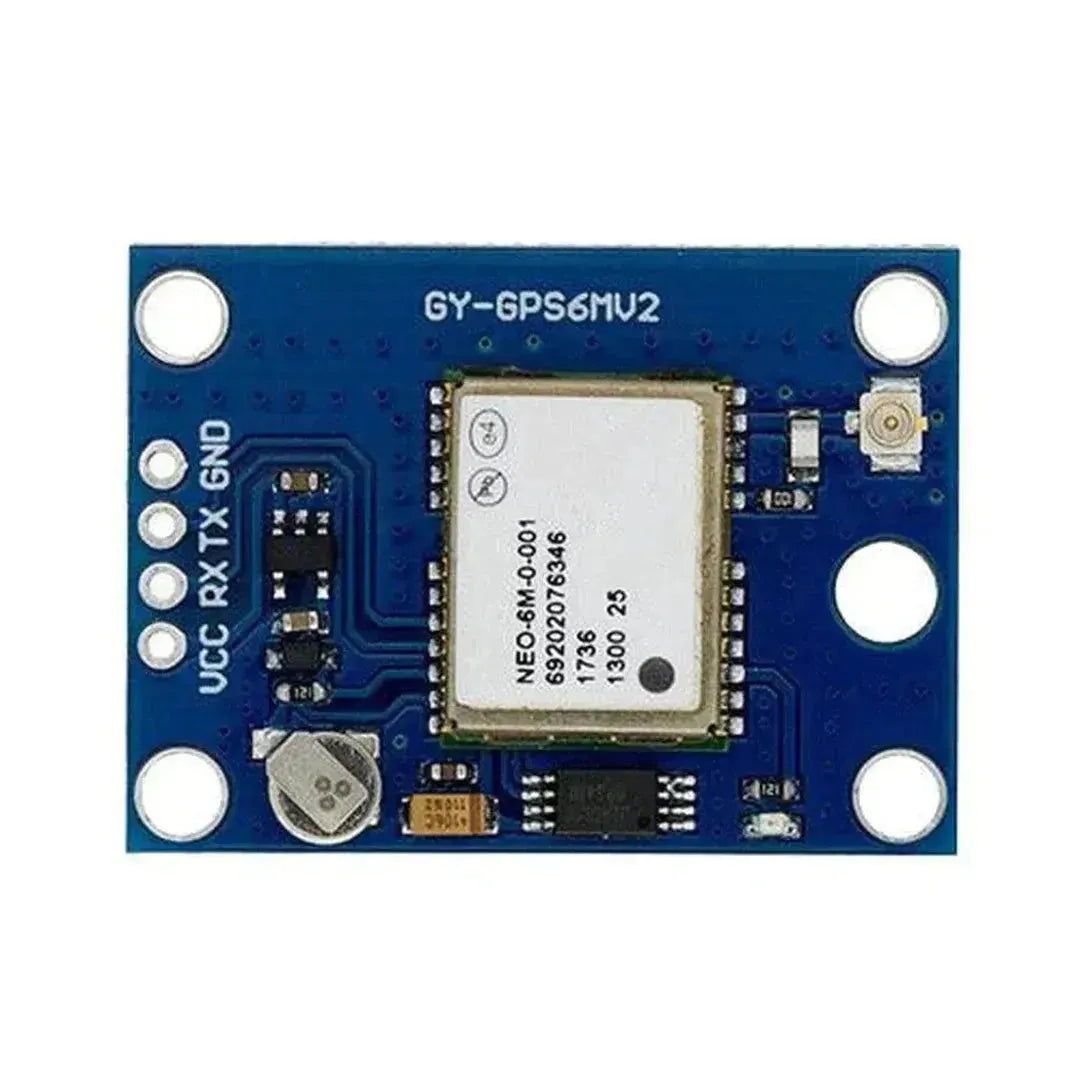
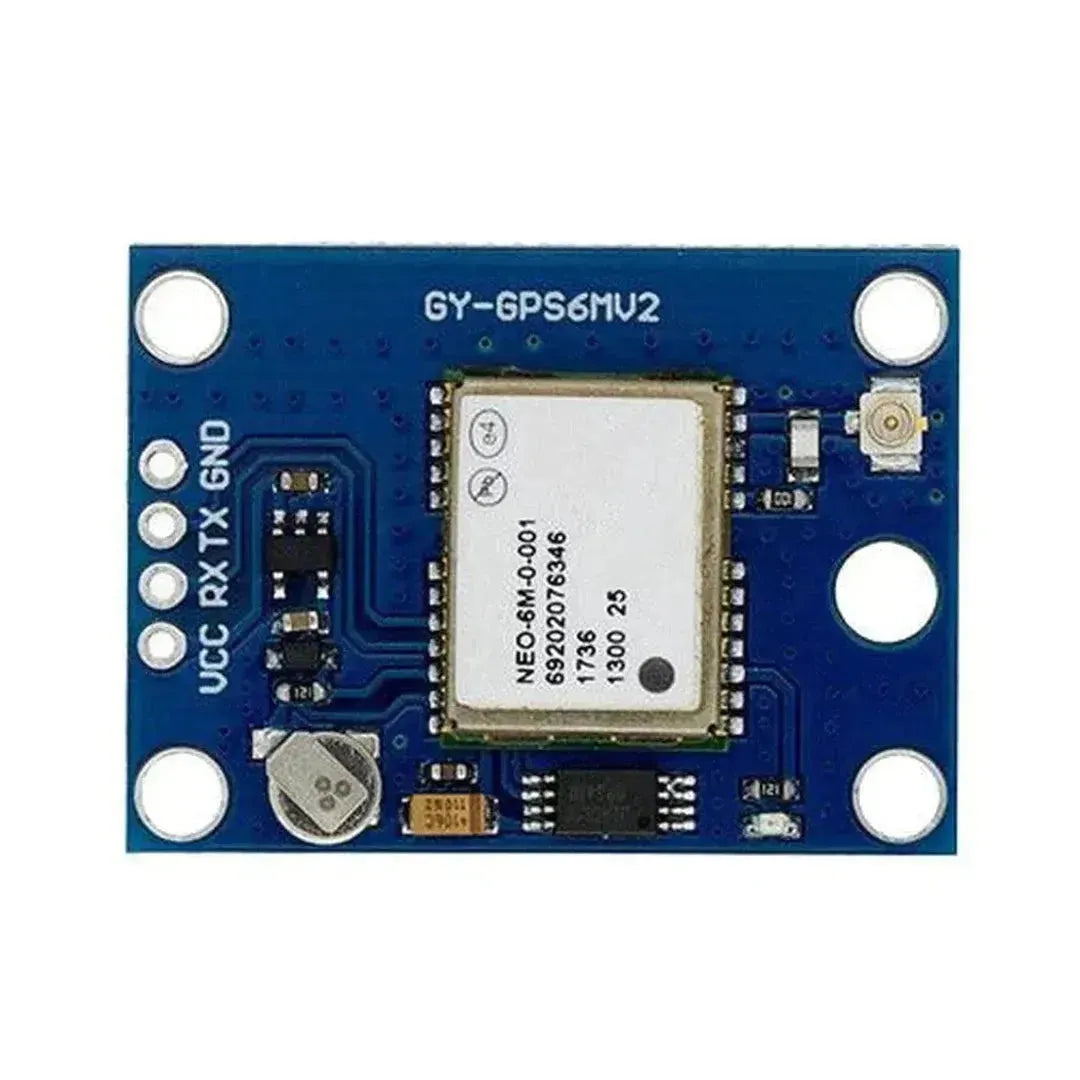
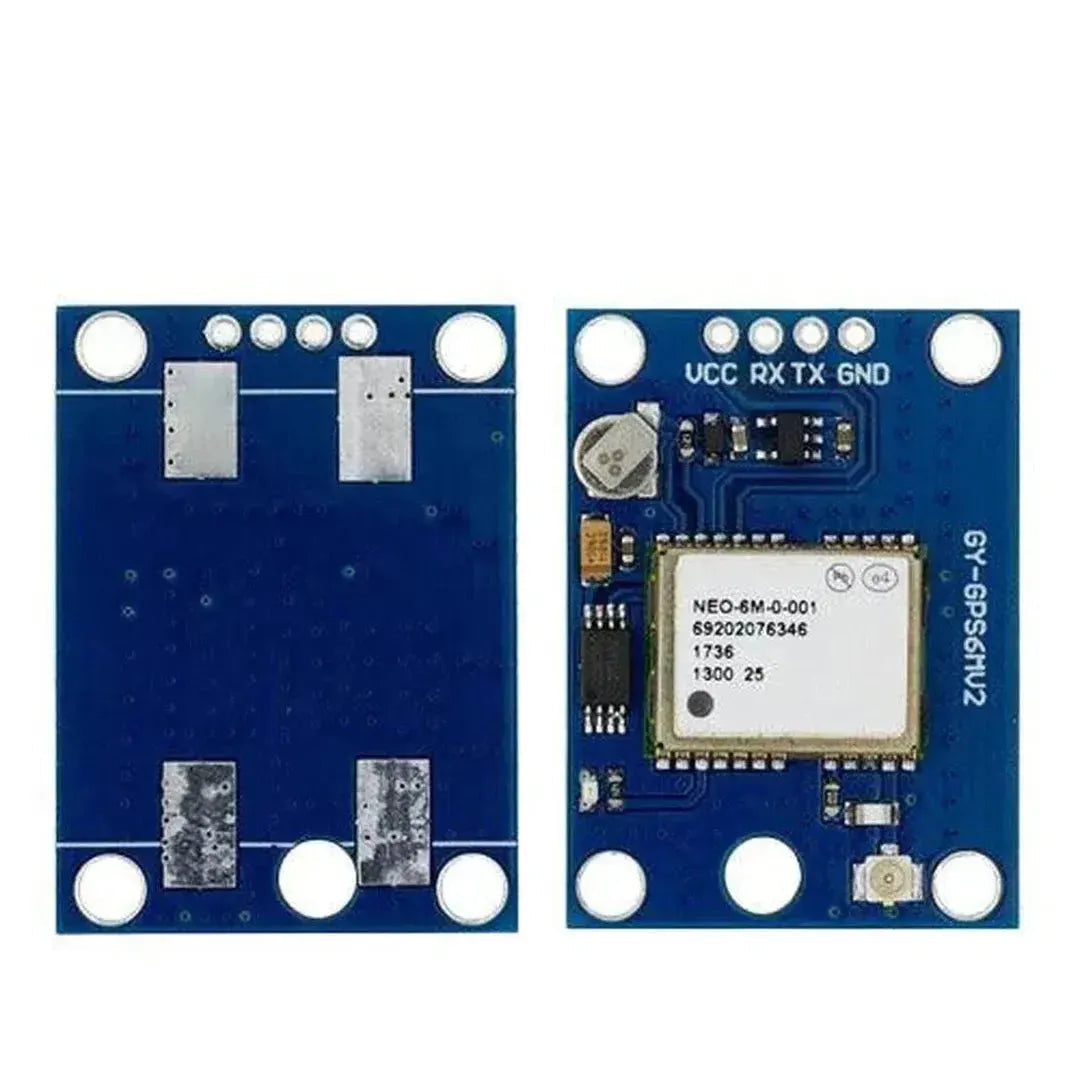
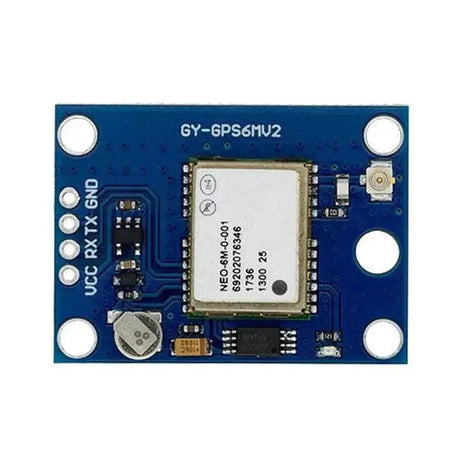
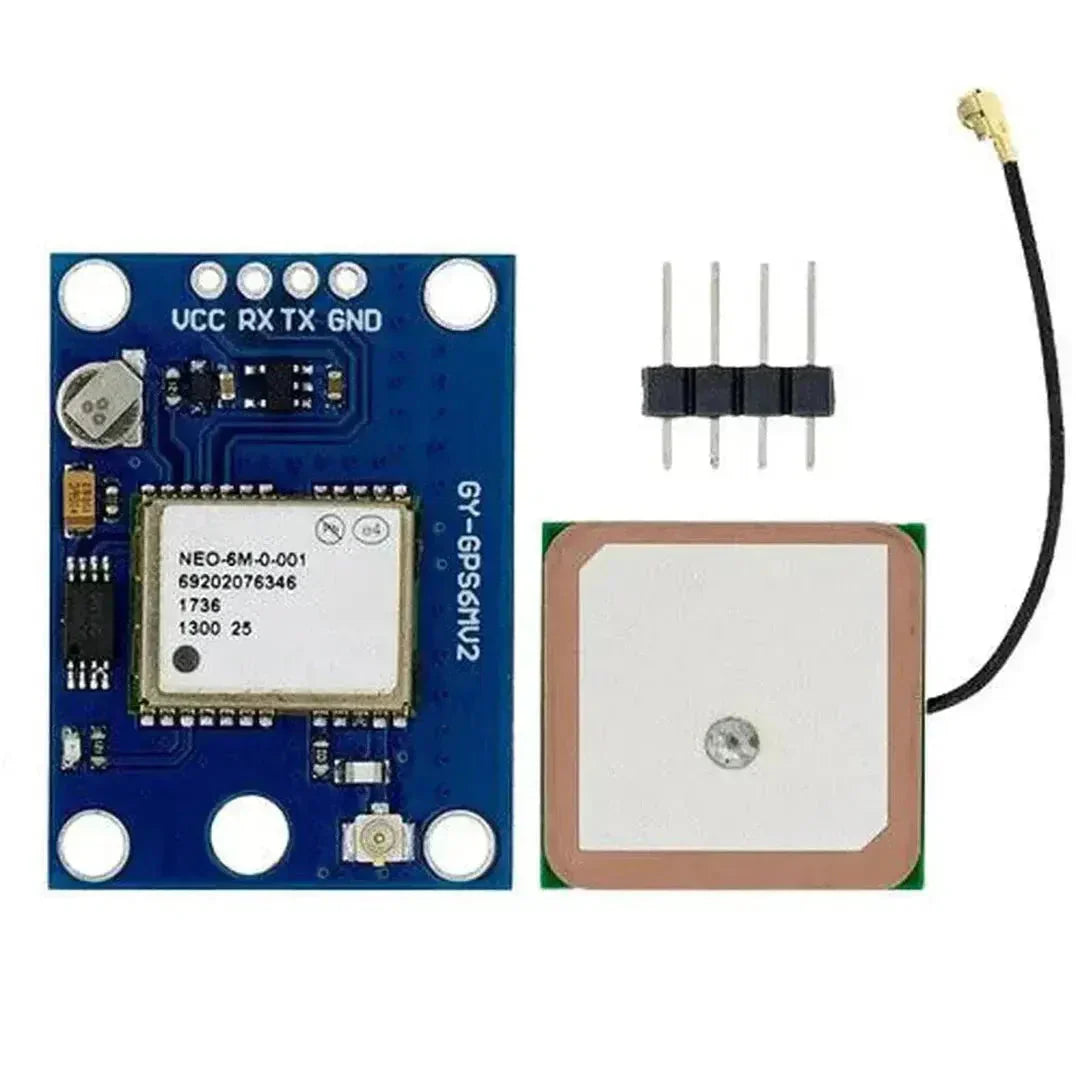
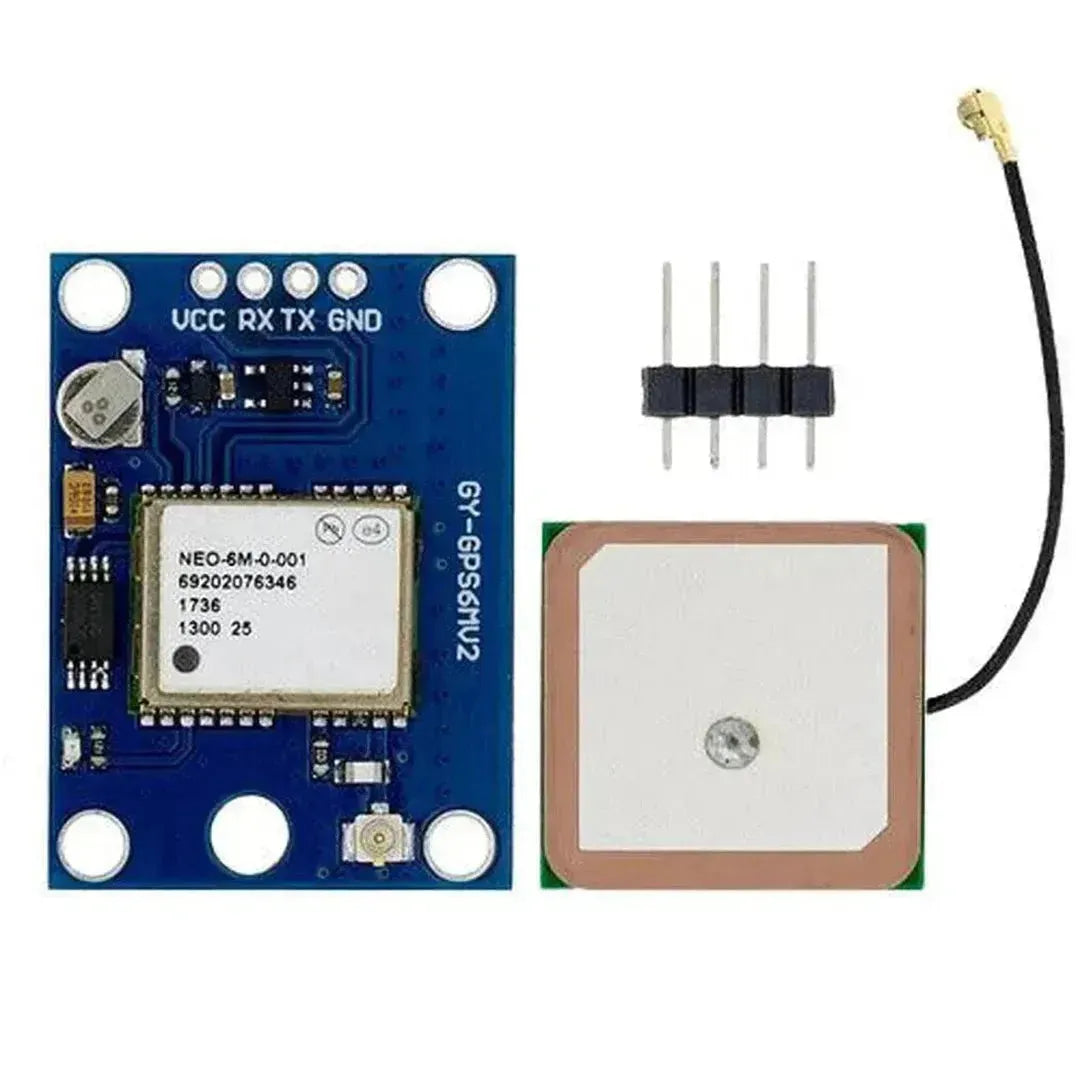
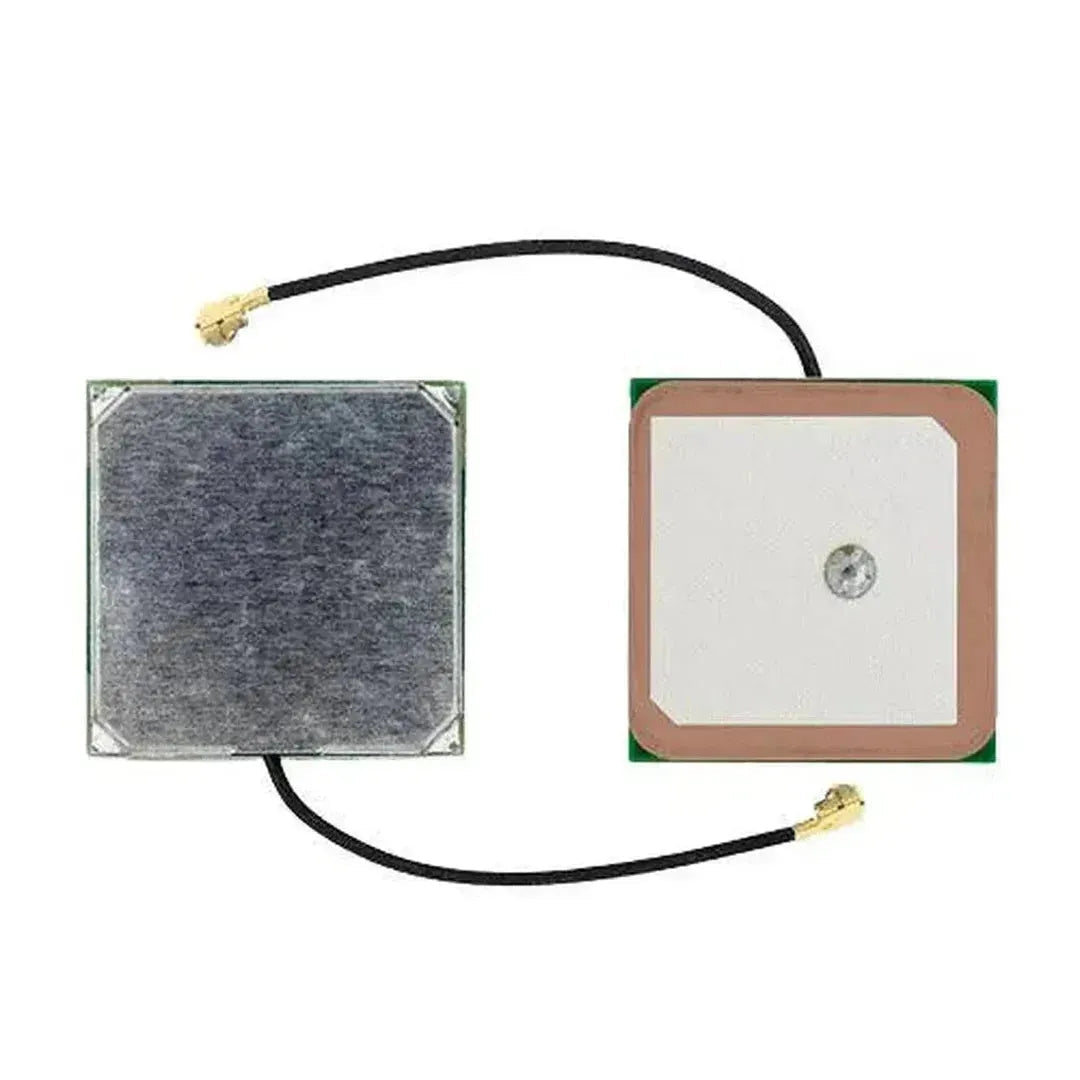
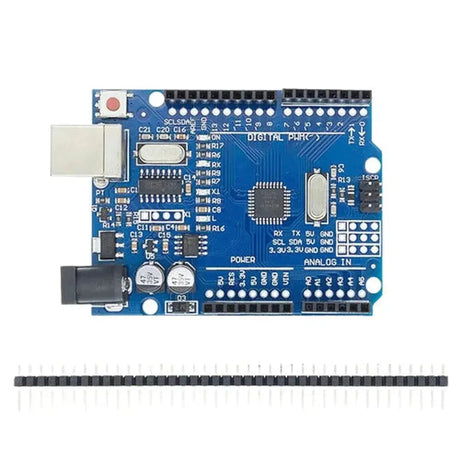
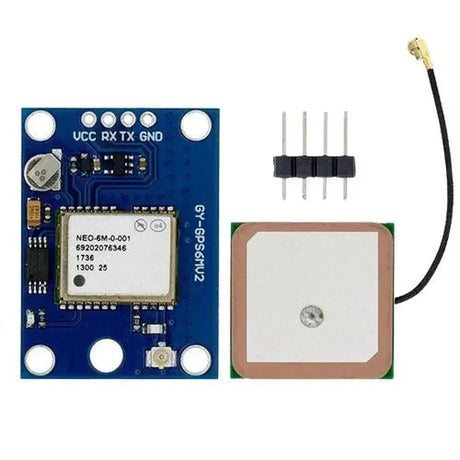
The NEO-6M GPS module is a highly popular and reliable GPS receiver module that provides accurate location, speed, and time data. It communicates using UART (serial) and is commonly used in navigation, tracking, and IoT projects. This tutorial will walk you through how to interface the NEO-6M GPS module with an Arduino.
What You Will Need
- NEO-6M GPS Module
- Arduino Board (e.g., Uno, Mega, Nano)
- Breadboard
- Jumper Wires
- A computer with the Arduino IDE installed
Step 1: Understanding the NEO-6M GPS Module
The NEO-6M GPS module has the following key pins:
| Pin | Function |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power Supply (3.3V or 5V) |
| GND | Ground |
| TX | Transmit Data |
| RX | Receive Data |
Note: The module includes an onboard antenna and may feature a connector for an external antenna to improve reception.
Step 2: Wiring the NEO-6M GPS to Arduino
Below is the wiring guide for connecting the NEO-6M module to the Arduino Uno:
| NEO-6M Pin | Arduino Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| TX | Pin 4 |
| RX | Pin 3 |
Important: The TX of the GPS module connects to the RX of the Arduino, and the RX of the GPS module connects to the TX of the Arduino. This is essential for proper communication.
Step 3: Install the TinyGPS++ Library
The TinyGPS++ library simplifies parsing GPS data, such as latitude, longitude, and time.
- Open the Arduino IDE.
- Go to Sketch > Include Library > Manage Libraries.
- Search for "TinyGPS++" in the Library Manager.
- Select the library and click Install.
Step 4: Upload the Code
Here is an example code to read and display GPS data:
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define GPS pins
#define RXPin 3
#define TXPin 4
// Set GPS baud rate
#define GPSBaud 9600
// Create GPS and Serial objects
TinyGPSPlus gps;
SoftwareSerial gpsSerial(RXPin, TXPin);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
gpsSerial.begin(GPSBaud);
Serial.println("NEO-6M GPS Module Test");
}
void loop() {
// Read GPS data
while (gpsSerial.available() > 0) {
gps.encode(gpsSerial.read());
if (gps.location.isUpdated()) {
Serial.print("Latitude: ");
Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6);
Serial.print(", Longitude: ");
Serial.println(gps.location.lng(), 6);
Serial.print("Date: ");
Serial.print(gps.date.day());
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(gps.date.month());
Serial.print("/");
Serial.println(gps.date.year());
Serial.print("Time: ");
Serial.print(gps.time.hour());
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(gps.time.minute());
Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(gps.time.second());
Serial.println("---------------------");
}
}
}
Step 5: Test the Setup
- Connect the Arduino to your computer via USB.
- Open the Arduino IDE and select the correct Board and Port under the Tools menu.
- Upload the code to the Arduino by clicking Upload.
- Open the Serial Monitor (Tools > Serial Monitor) and set the baud rate to
9600. - Place the GPS module near a window or outside for better signal reception. You should start seeing latitude, longitude, date, and time data in the Serial Monitor.
Troubleshooting
- No data or empty output: Ensure the GPS module is in an open area with a clear view of the sky. Check your wiring and ensure TX/RX connections are correct.
- Data updates slowly: Wait for the GPS module to get a satellite lock, which can take a few minutes in some cases.
- Garbage data: Verify that the baud rate in the code matches the module’s default baud rate (usually 9600).
Applications of the NEO-6M GPS Module
- Vehicle tracking systems
- Outdoor navigation
- Time synchronization for IoT devices
- Geofencing applications
Conclusion
You’ve successfully interfaced the NEO-6M GPS module with an Arduino and retrieved real-time location and time data. With this setup, you can build various GPS-based projects such as navigation systems or IoT trackers. Start exploring the possibilities!