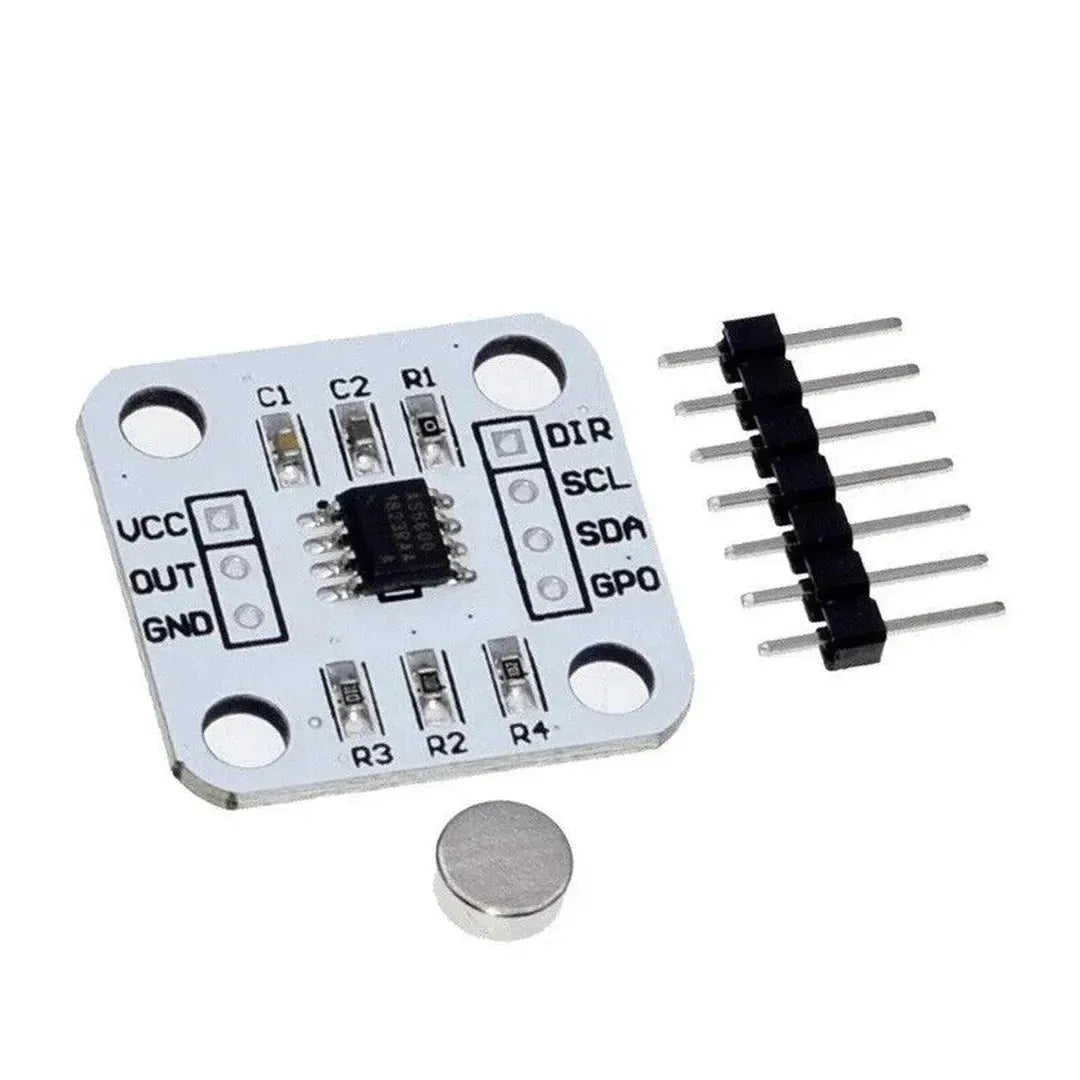
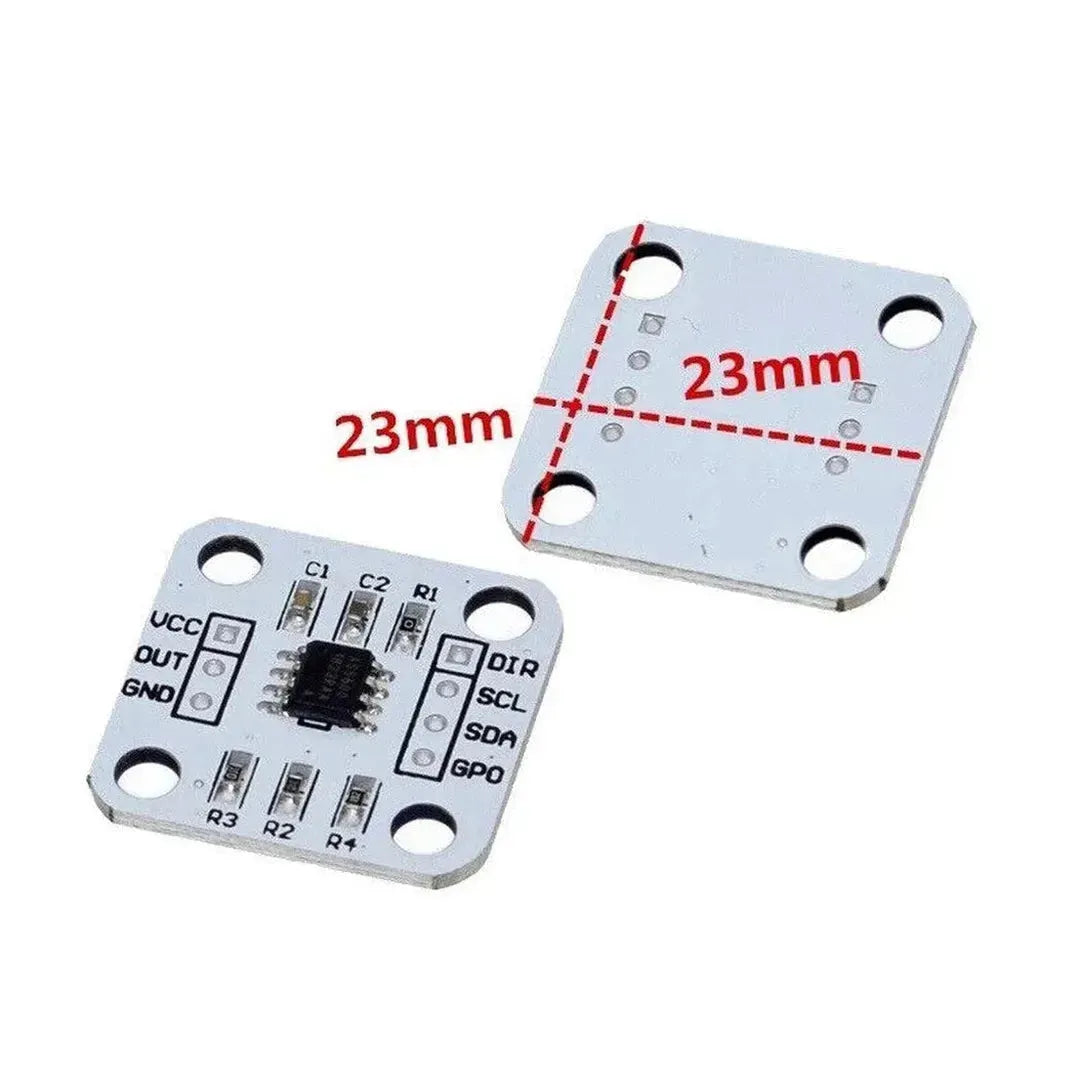
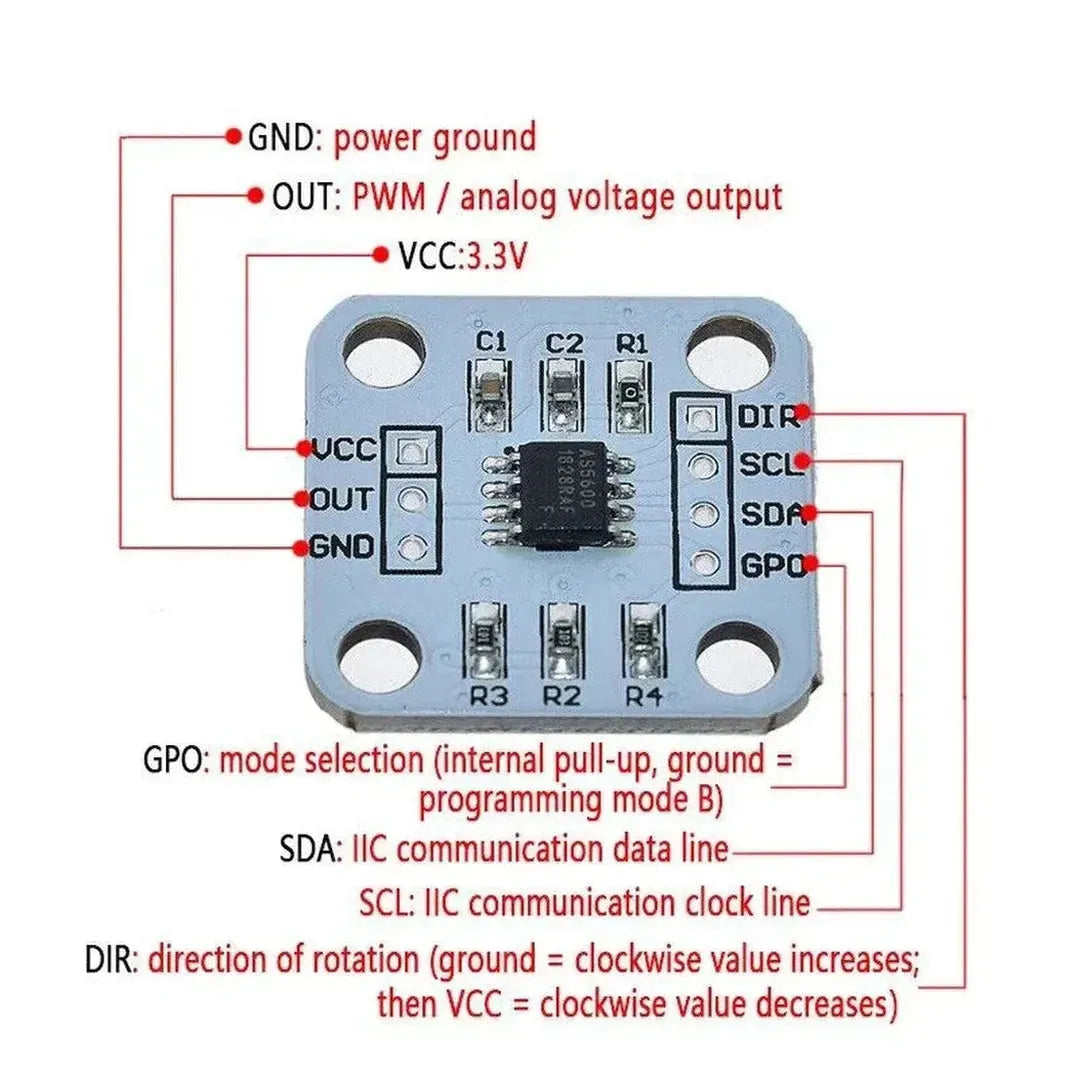
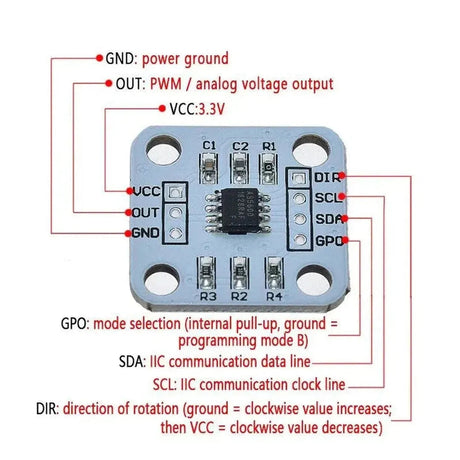
The AS5600 is a high-resolution rotary magnetic position sensor that can measure angles up to 360°. With its I2C interface, it is easy to integrate with a Raspberry Pi for precise angle measurements in robotics, automation, and other applications. This guide explains how to use the AS5600 with a Raspberry Pi to read angular positions.
What You Will Need
- Raspberry Pi (any model with I2C support, e.g., Pi 3, Pi 4)
- AS5600 Magnetic Rotary Encoder Module
- Magnet (diametrically magnetized)
- Breadboard and Jumper Wires
- A computer with SSH access to the Raspberry Pi or a connected keyboard and monitor
- Python installed on the Raspberry Pi
Step 1: Enable I2C on the Raspberry Pi
- Open the terminal on your Raspberry Pi.
- Run the Raspberry Pi configuration tool:
sudo raspi-config - Navigate to Interface Options > I2C, and enable it.
- Reboot the Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
Step 2: Wiring the AS5600 to the Raspberry Pi
The AS5600 uses the I2C protocol for communication. Connect it to the Raspberry Pi as follows:
| AS5600 Pin | Raspberry Pi Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V (Pin 1) |
| GND | Ground (Pin 6) |
| SDA | SDA (Pin 3, GPIO2) |
| SCL | SCL (Pin 5, GPIO3) |
Note: Ensure the AS5600 module's operating voltage matches the Raspberry Pi's 3.3V logic level.
Step 3: Install Required Tools and Libraries
- Update the Raspberry Pi:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y - Install I2C tools:
sudo apt install -y i2c-tools - Install Python libraries for I2C communication:
pip install smbus2
Step 4: Verify I2C Connection
- Detect the AS5600 on the I2C bus:
sudo i2cdetect -y 1 - You should see a device address (e.g.,
0x36) in the output. If not, check your wiring.
Step 5: Read Data from the AS5600
The AS5600 provides 12-bit angle data through I2C. You can use the following Python script to read and display the angular position.
Python Code Example
import smbus2
import time
# Define I2C address and bus
AS5600_ADDR = 0x36
ANGLE_REG = 0x0E
bus = smbus2.SMBus(1)
def read_angle():
# Read two bytes from the angle register
raw_data = bus.read_i2c_block_data(AS5600_ADDR, ANGLE_REG, 2)
angle = (raw_data[0] << 8) | raw_data[1] # Combine MSB and LSB
angle = angle & 0x0FFF # Mask to 12 bits
return (angle / 4096.0) * 360.0 # Convert to degrees
try:
while True:
angle = read_angle()
print(f"Angle: {angle:.2f} degrees")
time.sleep(0.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Exiting...")
Step 6: Applications of the AS5600
The AS5600 is versatile and can be used in various projects:
- Robotics: Measure joint or wheel angles for precise control.
- Encoders: Create DIY rotary encoders for CNC machines or 3D printers.
- Knob Controls: Use as a high-resolution knob for volume or menu navigation.
- Position Tracking: Track angular positions in automation systems.
Troubleshooting
-
Device Not Detected:
- Verify SDA and SCL connections.
- Ensure I2C is enabled on the Raspberry Pi.
- Check the operating voltage of the AS5600.
-
Inaccurate Readings:
- Ensure the magnet is correctly aligned with the AS5600 sensor.
- Use a diametrically magnetized magnet for accurate measurements.
-
I2C Errors:
- Check for conflicting devices on the I2C bus using
i2cdetect. - Verify the AS5600's address matches the script.
- Check for conflicting devices on the I2C bus using
Conclusion
The AS5600 magnetic rotary position sensor is a powerful and easy-to-use tool for measuring angles. By following this guide, you can integrate the AS5600 with a Raspberry Pi to create precise rotational measurement systems for robotics, automation, and more. Experiment with different applications to unlock the full potential of this versatile sensor!