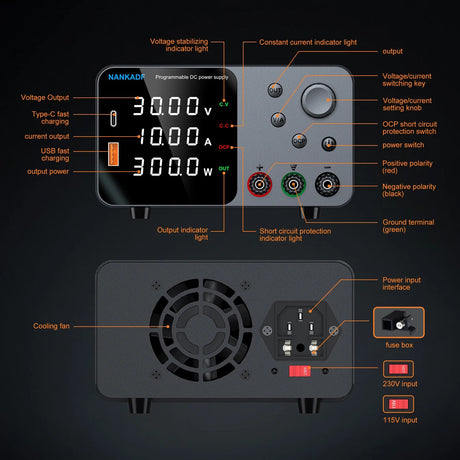
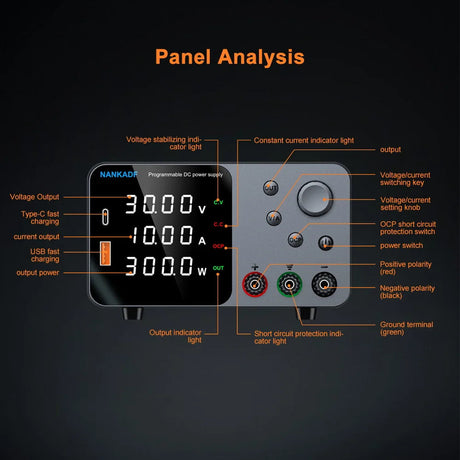
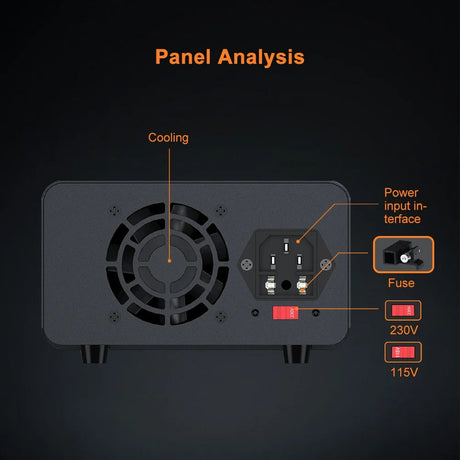
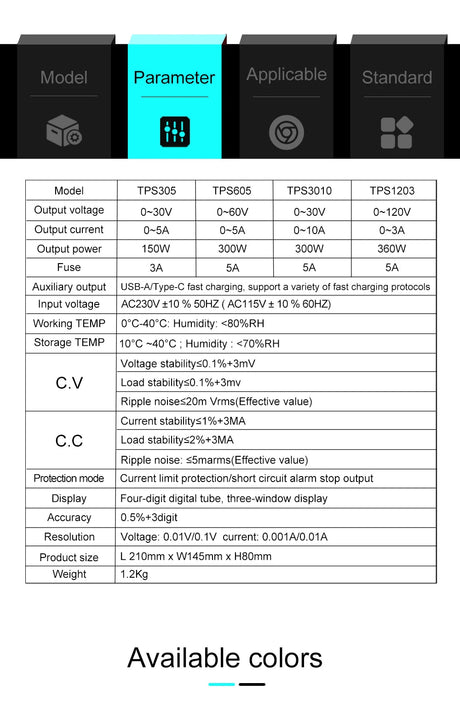
Arduino -ohjelmointi käyttää kontrollirakenteet kuten Jos, ja vaihtakaa kotelo Päätöksentekon ja silmukoiden hallitsemiseksi luonnoksessa. Nämä rakenteet sallivat Arduino reagoida olosuhteisiin, toista tehtäviä ja suorittaa erilaisia koodilohkoja syötteen perusteella.
1. Jos lausunto (ehdollinen suoritus)
Se Jos lausunto käytetään koodilohkon suorittamiseen Vain jos määritelty ehto täyttyy.
Syntaksi
if (condition) {
// Code to execute if condition is true
}
Esimerkki: LED: n kytkeminen päälle painikkeiden perusteella
const int buttonPin = 2; // Button connected to pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // LED connected to pin 13
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
int buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin); // Read button state
if (buttonState == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn LED on if button is pressed
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn LED off otherwise
}
}
If-Else-lausunto
if (temperature > 30) {
Serial.println("It's too hot!");
} else {
Serial.println("Temperature is normal.");
}
If-else if-lause
if (temperature > 30) {
Serial.println("It's too hot!");
} else if (temperature < 10) {
Serial.println("It's too cold!");
} else {
Serial.println("Temperature is comfortable.");
}
2. Silmukka (toistaa tehtävät kiinteä määrä kertoja)
Eräs Silmukka Suorittaa koodilohkon kiinteä määrä kertoja. Sitä käytetään yleisesti iteroivat taulukot tai toistuvien tehtävien hallinta.
Syntaksi
for (initialization; condition; increment) {
// Code to execute in each iteration
}
Esimerkki: LED: n vilkkuminen 5 kertaa
const int ledPin = 13;
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { // Loop runs 5 times
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn LED on
delay(500); // Wait 500 ms
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn LED off
delay(500);
}
delay(2000); // Pause before repeating
}
Esimerkki: juokseminen taulukon läpi
int numbers[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Serial.println(numbers[i]); // Print each number in the array
}
delay(2000);
}
3. silmukan ollessa (toistaminen, kunnes ehto täyttyy)
Eräs kun taas silmukka Suorittaa koodilohkon Niin kauan kuin määritelty tila pysyy totta.
Syntaksi
while (condition) {
// Code to execute while the condition is true
}
Esimerkki: Painikkeen odottaminen Paina
const int buttonPin = 2;
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Waiting for button press...");
while (digitalRead(buttonPin) == LOW) {
// Stay in loop until button is pressed
}
Serial.println("Button pressed!");
}
Esimerkki: Countdown -ajastin
int count = 10;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
while (count > 0) {
Serial.print("Countdown: ");
Serial.println(count);
count--;
delay(1000);
}
Serial.println("Liftoff!");
delay(5000); // Restart countdown after delay
count = 10; // Reset count
}
4
Eräs Kytkintapauslausunto käytetään kun Useita ehtoja on tarkistettava, tekee siitä vaihtoehdon if-else if-Else Ketjut.
Syntaksi
switch (variable) {
case value1:
// Code to execute if variable == value1
break;
case value2:
// Code to execute if variable == value2
break;
default:
// Code to execute if none of the cases match
}
Esimerkki: LEDin ohjaaminen kiertokytkimellä
const int ledPin = 13;
int mode = 1; // Example mode variable
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
switch (mode) {
case 1:
Serial.println("Mode 1: LED ON");
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
break;
case 2:
Serial.println("Mode 2: LED BLINKING");
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
delay(500);
break;
case 3:
Serial.println("Mode 3: LED OFF");
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
break;
default:
Serial.println("Invalid Mode");
break;
}
}
Esimerkki: painikkeen käyttäminen kierroksien läpi
const int buttonPin = 2;
int mode = 1;
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(buttonPin) == HIGH) {
mode++;
if (mode > 3) mode = 1; // Reset mode to 1 if it exceeds 3
delay(500); // Debounce delay
}
switch (mode) {
case 1:
Serial.println("Mode 1: Low Power Mode");
break;
case 2:
Serial.println("Mode 2: Normal Mode");
break;
case 3:
Serial.println("Mode 3: High Performance Mode");
break;
default:
Serial.println("Invalid Mode");
break;
}
}
Johtopäätös
- Jos lausunnot Salli ehdollisen suorituksen anturin lukemien tai painikkeen painikkeiden perusteella.
- silmukoihin ovat hyödyllisiä toistuvissa tehtävissä, joilla on tunnettu lukumäärä, kuten LEDin vilkkuminen.
- kun taas silmukot Suorita koodi jatkuvasti, kunnes tietty ehto täyttyy.
- Vaihda tapauslausekkeet Yksinkertaista päätöksentekoa käsitellessäsi useita ehtoja tehokkaasti.
Nämä rakenteet Paranna Arduino -ohjelmointia helpottamalla silmukoiden, olosuhteiden ja laitteen hallinnan hallintaa. 🚀