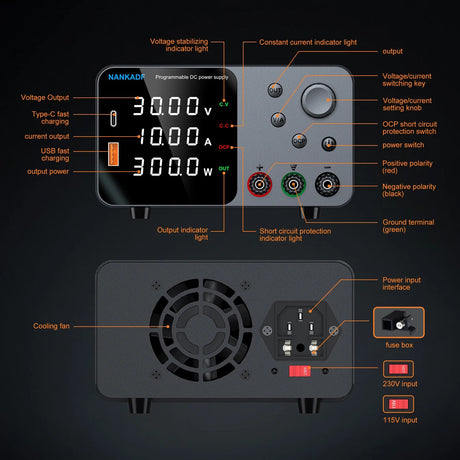
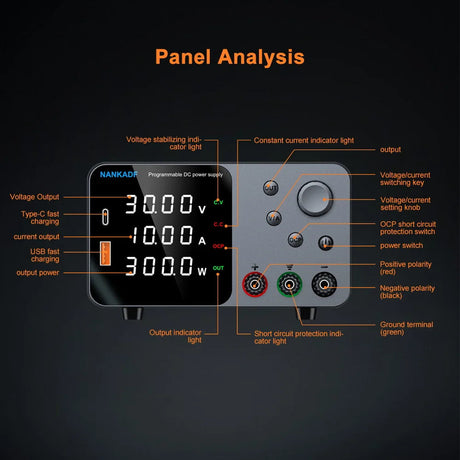
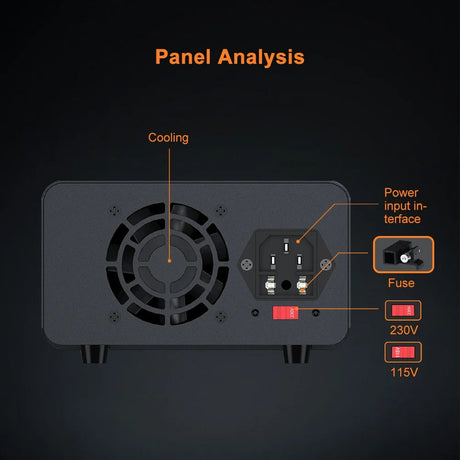
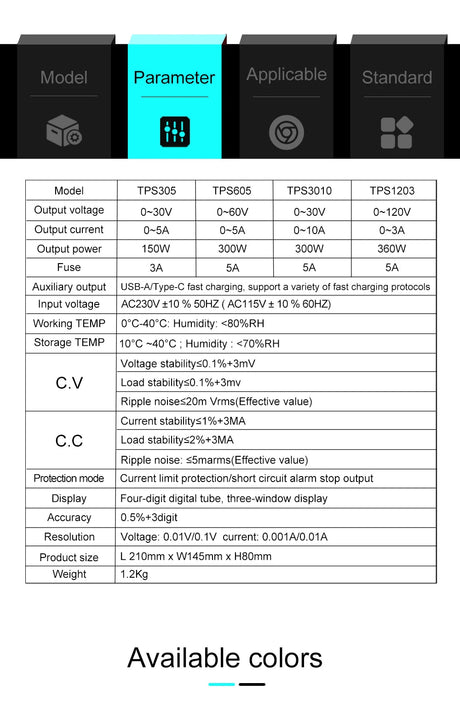
Arduinoプログラミングは使用します 制御構造 のような 場合、while、switchケース スケッチの意思決定とループを制御するため。これらの構造により Arduino 条件に応答するには、タスクを繰り返し、入力に基づいてさまざまなコードブロックを実行します。
1。IFステートメント(条件付き実行)
IFステートメント コードのブロックを実行するために使用されます 指定された条件が満たされている場合のみ.
構文
if (condition) {
// Code to execute if condition is true
}
例:ボタンを押すことに基づいてLEDをオンにする
const int buttonPin = 2; // Button connected to pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // LED connected to pin 13
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
int buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin); // Read button state
if (buttonState == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn LED on if button is pressed
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn LED off otherwise
}
}
if-elseステートメント
if (temperature > 30) {
Serial.println("It's too hot!");
} else {
Serial.println("Temperature is normal.");
}
if-else ifステートメント
if (temperature > 30) {
Serial.println("It's too hot!");
} else if (temperature < 10) {
Serial.println("It's too cold!");
} else {
Serial.println("Temperature is comfortable.");
}
2。ループの場合(繰り返しタスク固定回数の回数)
a ループ用 コードブロックを実行します 固定回数。一般的に使用されます アレイを繰り返したり、繰り返しタスクを制御したりします.
構文
for (initialization; condition; increment) {
// Code to execute in each iteration
}
例:LEDを5回点滅させます
const int ledPin = 13;
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { // Loop runs 5 times
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn LED on
delay(500); // Wait 500 ms
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn LED off
delay(500);
}
delay(2000); // Pause before repeating
}
例:配列を介して実行します
int numbers[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Serial.println(numbers[i]); // Print each number in the array
}
delay(2000);
}
3。ループ中(条件が満たされるまで繰り返す)
a ループ中 コードブロックを実行します 指定された条件が真実のままである限り.
構文
while (condition) {
// Code to execute while the condition is true
}
例:ボタンを押すのを待っています
const int buttonPin = 2;
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Waiting for button press...");
while (digitalRead(buttonPin) == LOW) {
// Stay in loop until button is pressed
}
Serial.println("Button pressed!");
}
例:カウントダウンタイマー
int count = 10;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
while (count > 0) {
Serial.print("Countdown: ");
Serial.println(count);
count--;
delay(1000);
}
Serial.println("Liftoff!");
delay(5000); // Restart countdown after delay
count = 10; // Reset count
}
4.スイッチケース(複数の条件を効率的に処理する)
a スイッチケースステートメント いつ使用されますか 複数の条件を確認する必要があります、代替品にします if-else if-else チェーン。
構文
switch (variable) {
case value1:
// Code to execute if variable == value1
break;
case value2:
// Code to execute if variable == value2
break;
default:
// Code to execute if none of the cases match
}
例:ロータリースイッチでLEDを制御します
const int ledPin = 13;
int mode = 1; // Example mode variable
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
switch (mode) {
case 1:
Serial.println("Mode 1: LED ON");
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
break;
case 2:
Serial.println("Mode 2: LED BLINKING");
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
delay(500);
break;
case 3:
Serial.println("Mode 3: LED OFF");
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
break;
default:
Serial.println("Invalid Mode");
break;
}
}
例:ボタンを使用してモードをサイクリングします
const int buttonPin = 2;
int mode = 1;
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(buttonPin) == HIGH) {
mode++;
if (mode > 3) mode = 1; // Reset mode to 1 if it exceeds 3
delay(500); // Debounce delay
}
switch (mode) {
case 1:
Serial.println("Mode 1: Low Power Mode");
break;
case 2:
Serial.println("Mode 2: Normal Mode");
break;
case 3:
Serial.println("Mode 3: High Performance Mode");
break;
default:
Serial.println("Invalid Mode");
break;
}
}
結論
- ステートメントの場合 センサーの測定値またはボタンプレスに基づいて条件付き実行を許可します。
- ループ用 LEDを点滅させるなど、既知のカウントを持つ反復タスクに役立ちます。
- ループ中 特定の条件が満たされるまでコードを継続的に実行します。
- ケースステートメントを切り替えます 複数の条件を効率的に処理するときに意思決定を簡素化します。
これらの構造 Arduinoプログラミングを強化します ループ、条件、およびデバイス制御を簡単に管理できるようにすることにより。 🚀