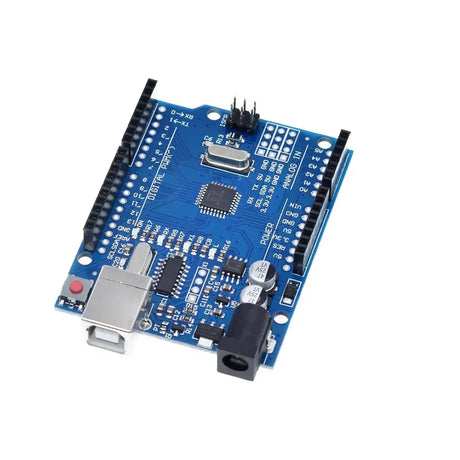
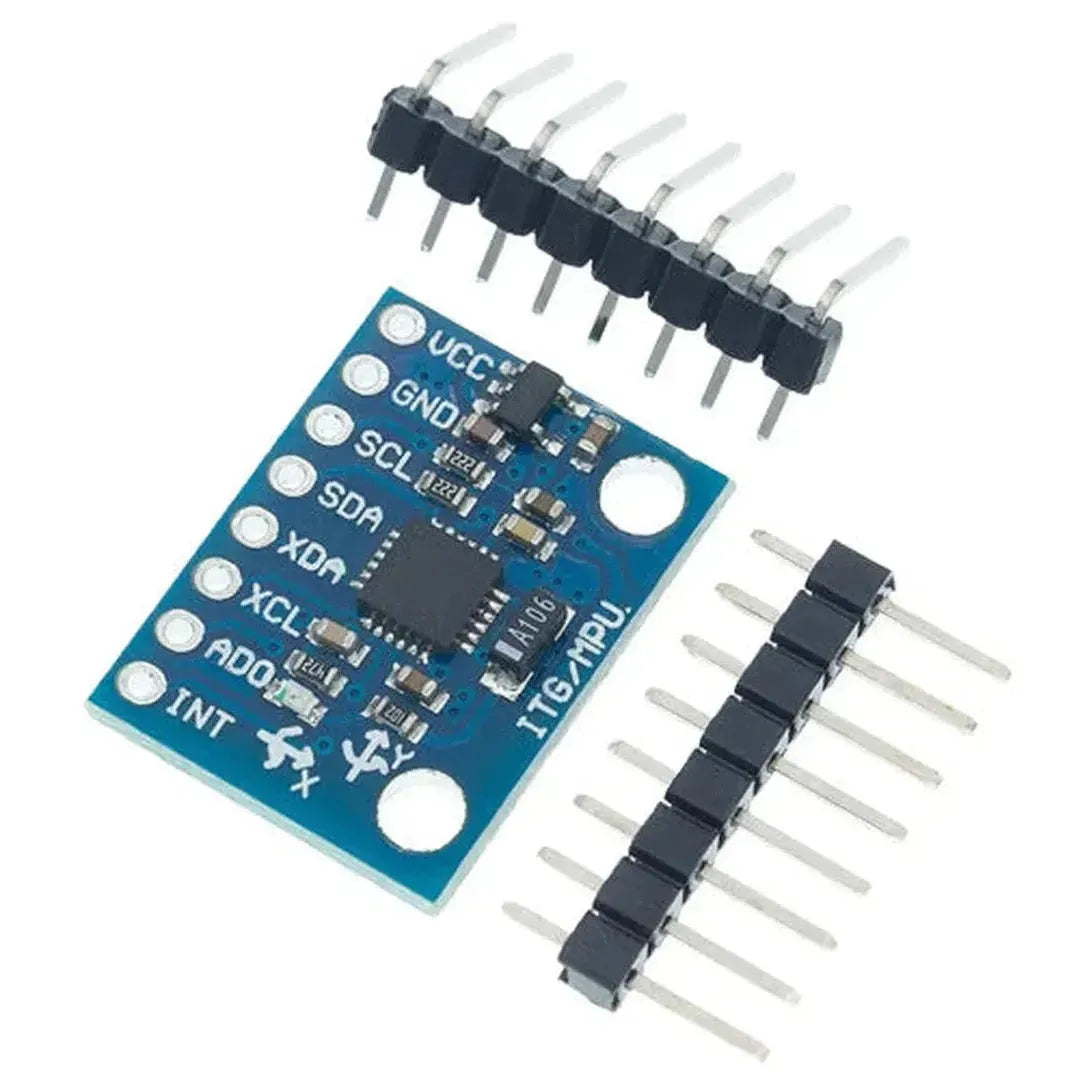
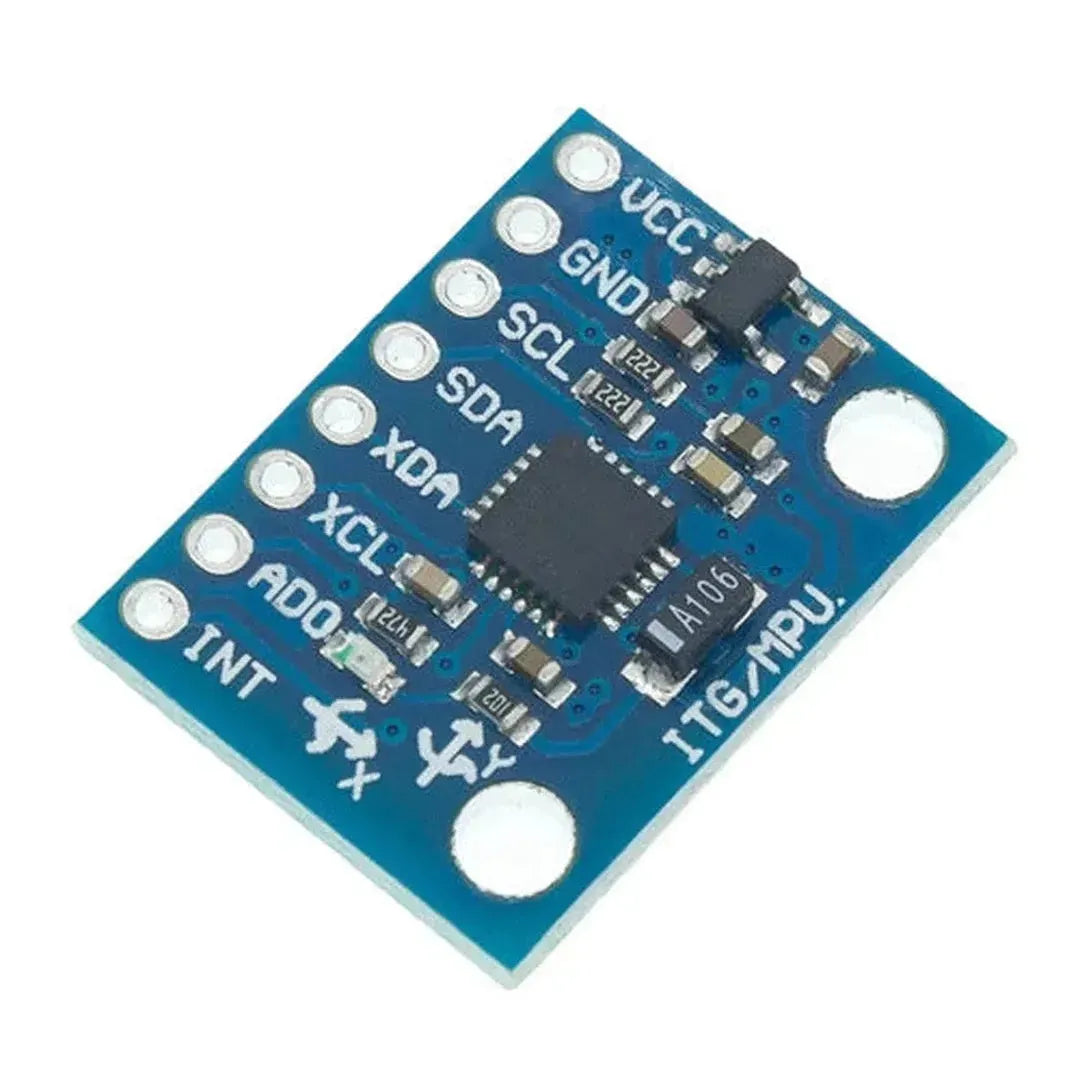
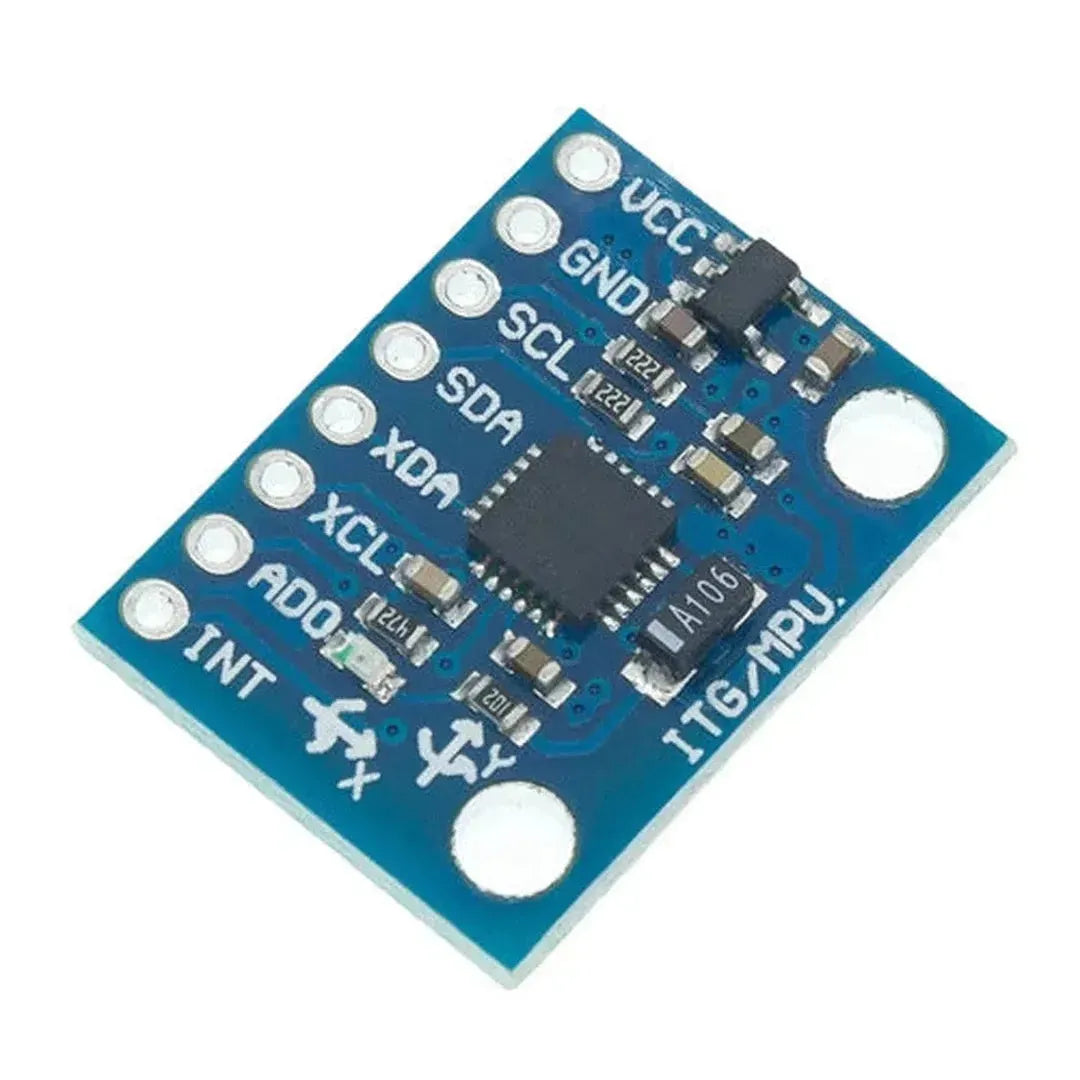
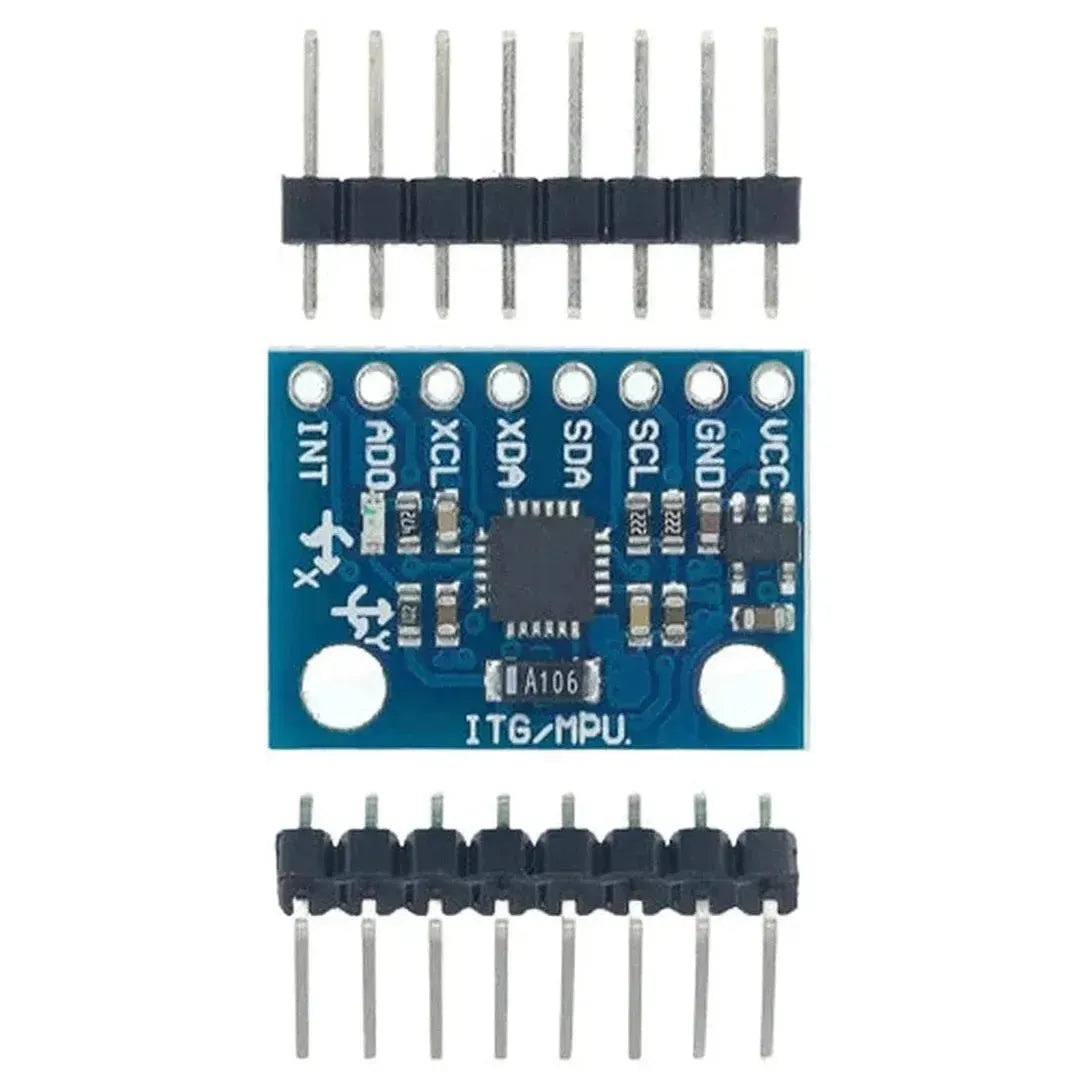
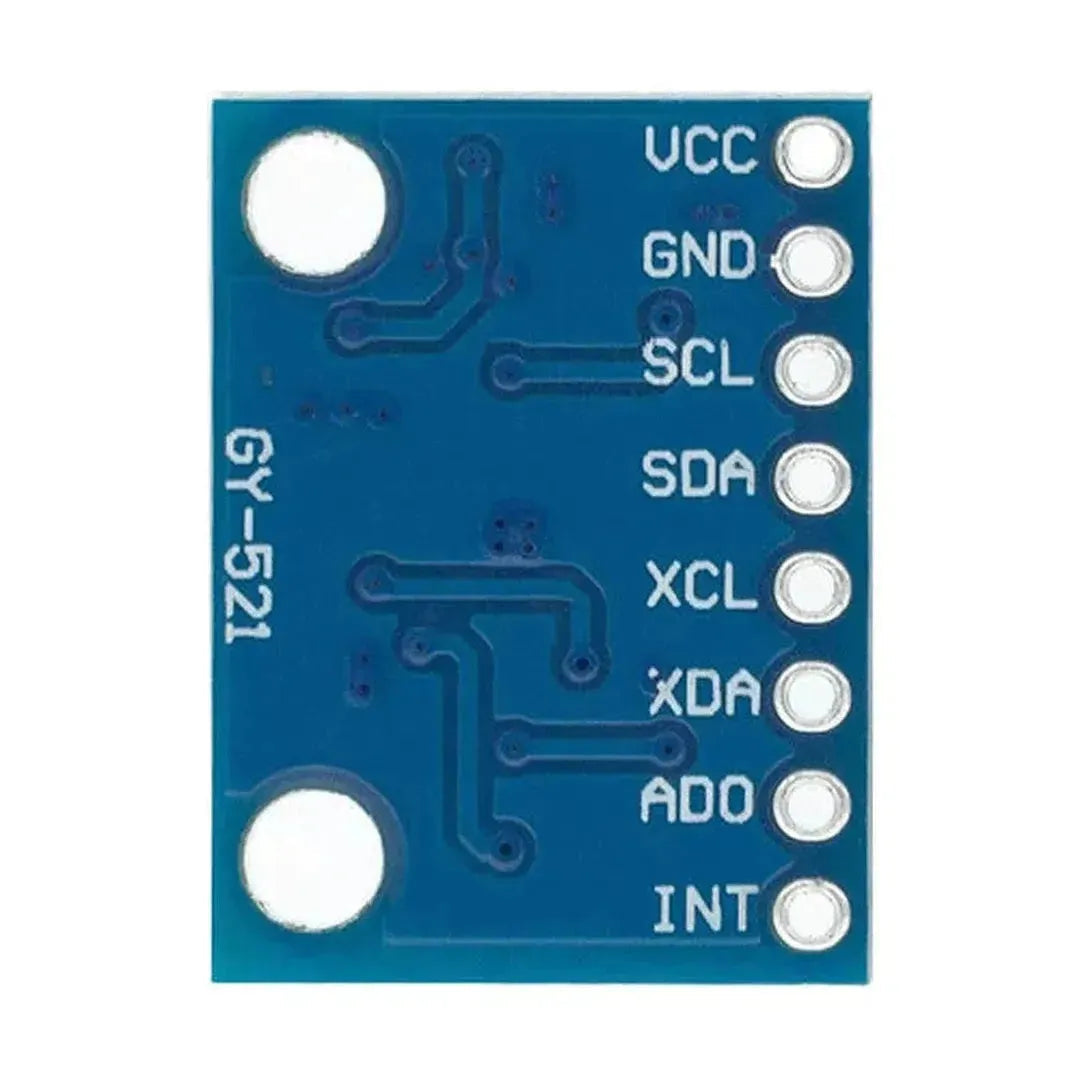
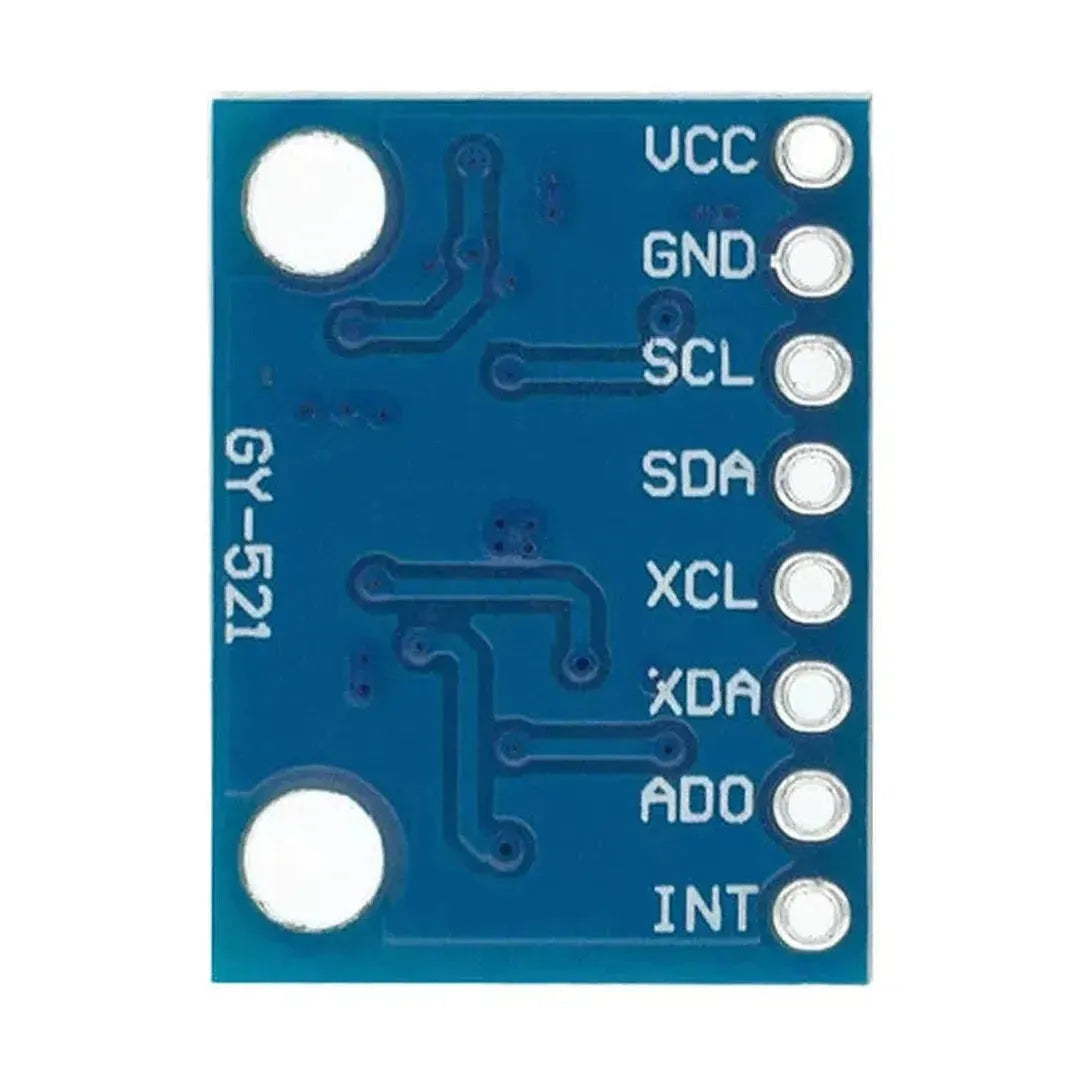
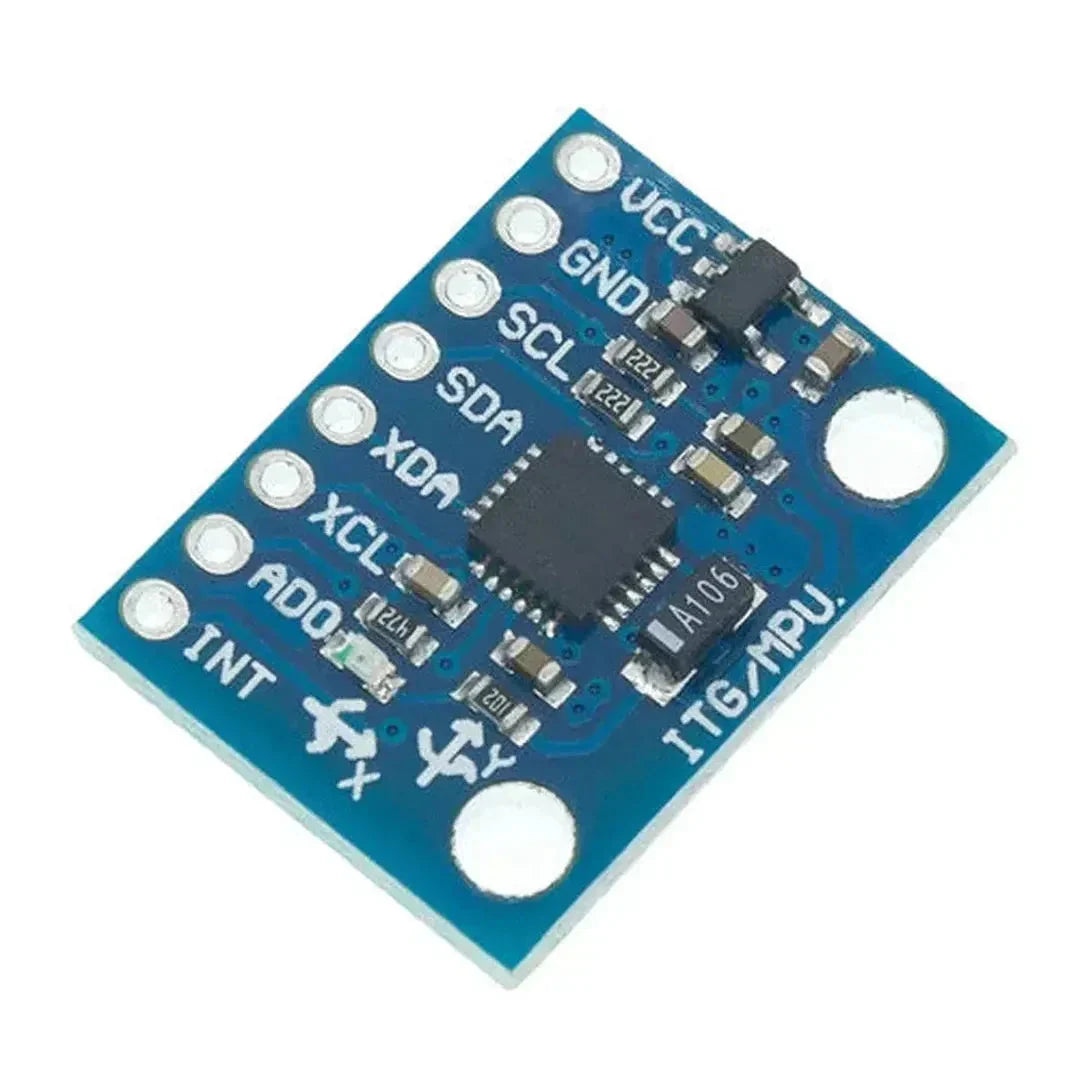
The MPU6050 is a versatile and affordable sensor that combines a 3-axis accelerometer and a 3-axis gyroscope into a single package. It communicates via the I2C interface and is perfect for motion tracking, balancing robots, and gesture-based controls. This tutorial will show you how to interface the MPU6050 with an Arduino.
What You Will Need
- MPU6050 Module
- Arduino Board (e.g., Uno, Mega, Nano)
- Breadboard
- Jumper Wires
- A computer with the Arduino IDE installed
Step 1: Wiring the MPU6050 to Arduino
The MPU6050 uses the I2C protocol, requiring only two data lines: SDA (data) and SCL (clock). Here are the typical connections:
| MPU6050 Pin | Arduino Uno Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| SDA | A4 (SDA) |
| SCL | A5 (SCL) |
Note: Check your specific Arduino board’s I2C pinout if you’re using a different model.
Step 2: Install the MPU6050 Library
To make it easier to interface with the MPU6050, we’ll use the "MPU6050" library.
- Open the Arduino IDE.
- Go to Sketch > Include Library > Manage Libraries.
- In the Library Manager, search for "MPU6050 by Electronic Cats".
- Select the library and click Install.
Step 3: Upload the Code
Here’s a basic example to read accelerometer and gyroscope data from the MPU6050:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <MPU6050.h>
MPU6050 mpu;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
Serial.println("Initializing MPU6050...");
if (!mpu.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to find MPU6050 sensor!");
while (1) {
delay(10);
}
}
Serial.println("MPU6050 Initialized.");
}
void loop() {
mpu.update();
Serial.print("Accel X: ");
Serial.print(mpu.getAccX());
Serial.print(" | Accel Y: ");
Serial.print(mpu.getAccY());
Serial.print(" | Accel Z: ");
Serial.println(mpu.getAccZ());
Serial.print("Gyro X: ");
Serial.print(mpu.getGyroX());
Serial.print(" | Gyro Y: ");
Serial.print(mpu.getGyroY());
Serial.print(" | Gyro Z: ");
Serial.println(mpu.getGyroZ());
delay(500); // Update every 500ms
}
Step 4: Test the Setup
- Connect your Arduino to the computer using a USB cable.
- Open the Arduino IDE and select the correct Board and Port from the Tools menu.
- Upload the code by clicking the Upload button.
- Open the Serial Monitor (Tools > Serial Monitor) and set the baud rate to
9600. - You should see live accelerometer and gyroscope readings displayed.
Understanding the Data
- Accelerometer (Accel X, Y, Z): Measures linear acceleration in three axes.
- Gyroscope (Gyro X, Y, Z): Measures angular velocity (rotation speed) around three axes.
Troubleshooting
- Sensor not detected: Double-check the wiring and ensure the I2C lines are correctly connected.
- No output on Serial Monitor: Verify the baud rate matches the code setting (9600).
- Incorrect readings: Keep the sensor level during initialization to prevent drift.
Applications of MPU6050
- Balancing robots
- Gesture recognition
- Motion tracking for VR/AR
- Fitness tracking devices
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully interfaced the MPU6050 with an Arduino and read real-time motion data. This sensor is incredibly versatile and can be used in countless projects. Try integrating the MPU6050 into your next motion-based project and unleash its potential!