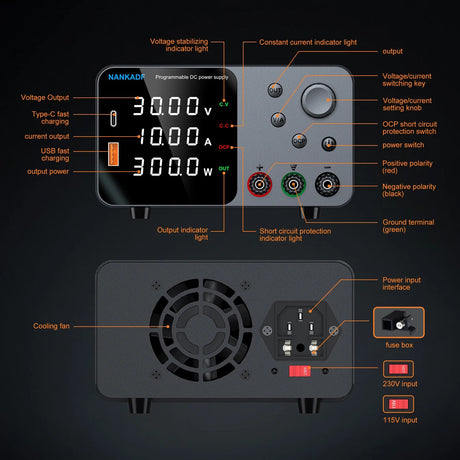
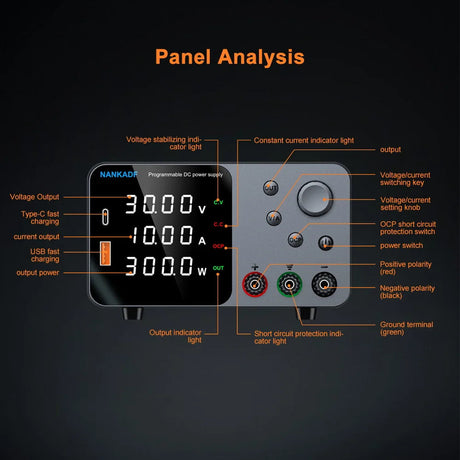
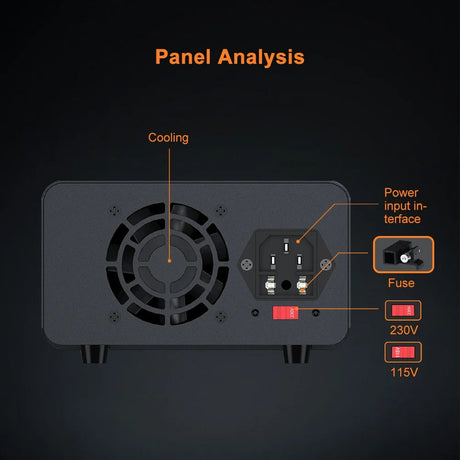
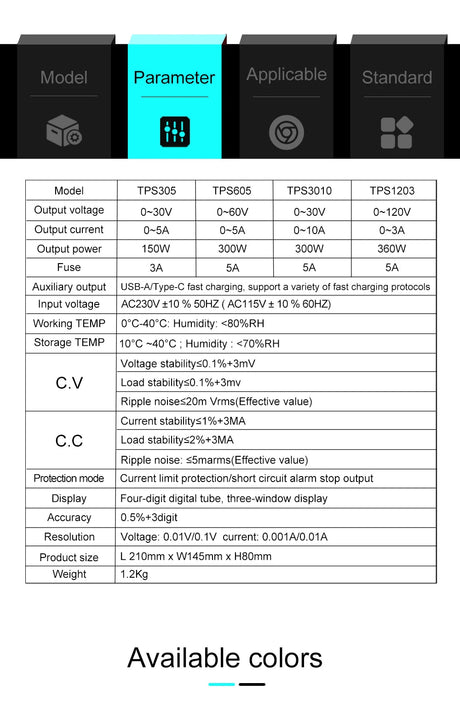
Node-RED is a powerful and flexible visual programming tool for connecting devices, APIs, and services. By running Node-RED on a Raspberry Pi, you can automate tasks, process IoT data, and build interactive workflows. This guide will walk you through setting up and running Node-RED on a Raspberry Pi.
What You Will Need
- Raspberry Pi (any model with GPIO support, e.g., Pi 3, Pi 4)
- MicroSD Card (at least 8GB, Class 10 or better)
- Power Supply (5V, 2.5A minimum for Pi 3; 5V, 3A for Pi 4)
- Raspberry Pi OS (Lite or Desktop version)
- Internet Connection
Step 1: Update the Raspberry Pi
- Ensure your Raspberry Pi is up to date:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Step 2: Install Node-RED
The recommended way to install Node-RED on a Raspberry Pi is via the official installation script.
-
Run the Node-RED installation script:
bash <(curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/node-red/linux-installers/master/deb/update-nodejs-and-nodered) -
Allow the script to complete the installation. This will:
- Install or update Node.js
- Install or update Node-RED
- Configure Node-RED to run as a service
-
After the installation, start Node-RED:
node-red-start -
To ensure Node-RED starts automatically on boot, enable the service:
sudo systemctl enable nodered.service
Step 3: Access the Node-RED Interface
-
Determine the Raspberry Pi’s IP address:
hostname -I -
Open a web browser on a device connected to the same network and navigate to:
http://<raspberry-pi-ip>:1880 -
You will see the Node-RED editor interface.
Step 4: Build Your First Flow
- Add a Node: Drag and drop nodes from the palette on the left.
- Connect Nodes: Link the output of one node to the input of another.
- Configure Nodes: Double-click on a node to configure its properties.
- Deploy the Flow: Click the Deploy button in the top-right corner to activate your flow.
Example: Create a simple flow to inject a timestamp and log it to the debug console.
- Drag an Inject node and a Debug node onto the workspace.
- Connect them with a line.
- Deploy the flow and click the button on the Inject node to see the output in the debug panel.
Step 5: Extend Node-RED with Additional Nodes
- Open the Manage Palette option from the menu in the top-right corner.
- Browse and install additional nodes to extend Node-RED's capabilities, such as:
- node-red-dashboard: Create web-based dashboards.
- node-red-contrib-mqtt: Connect to MQTT brokers.
- node-red-node-email: Send and receive emails.
Step 6: Applications of Node-RED
- IoT Automation: Connect sensors and actuators for smart home projects.
- Data Processing: Process and visualize real-time data from APIs or devices.
- Home Automation: Integrate with platforms like Home Assistant or OpenHAB.
- Notifications: Send alerts via email, SMS, or messaging apps like Telegram.
Troubleshooting
-
Node-RED Not Accessible:
- Ensure the Node-RED service is running:
sudo systemctl status nodered.service - Verify the IP address and port (default:
1880).
- Ensure the Node-RED service is running:
-
Node Installation Errors:
- Ensure Node.js is up to date:
node -v - Reinstall problematic nodes using the Manage Palette.
- Ensure Node.js is up to date:
-
Performance Issues:
- Reduce the number of active flows or deploy them on a more powerful Raspberry Pi model (e.g., Pi 4).
Conclusion
Node-RED is a powerful tool for creating and automating workflows with minimal programming knowledge. Running it on a Raspberry Pi provides a low-cost platform for IoT projects, data visualization, and home automation. Follow this guide to set up Node-RED and start exploring its endless possibilities!